Role of TRP Channels in Liver-Related Diseases
- PMID: 37569884
- PMCID: PMC10420300
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512509
Role of TRP Channels in Liver-Related Diseases
Abstract
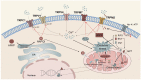
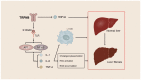
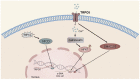
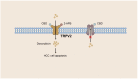
The liver plays a crucial role in preserving the homeostasis of an entire organism by metabolizing both endogenous and exogenous substances, a process that relies on the harmonious interactions of hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), Kupffer cells (KCs), and vascular endothelial cells (ECs). The disruption of the liver's normal structure and function by diverse pathogenic factors imposes a significant healthcare burden. At present, most of the treatments for liver disease are palliative in nature, rather than curative or restorative. Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, which are extensively expressed in the liver, play a crucial role in regulating intracellular cation concentration and serve as the origin or intermediary stage of certain signaling pathways that contribute to liver diseases. This review provides an overview of recent developments in liver disease research, as well as an examination of the expression and function of TRP channels in various liver cell types. Furthermore, we elucidate the molecular mechanism by which TRP channels mediate liver injury, liver fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ultimately, the present discourse delves into the current state of research and extant issues pertaining to the targeting of TRP channels in the treatment of liver diseases and other ailments. Despite the numerous obstacles encountered, TRP channels persist as an extremely important target for forthcoming clinical interventions aimed at treating liver diseases.
Keywords: TRP channels; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver diseases; liver fibrosis; liver injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and function of TRP channels in liver cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;704:667-86. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-0265-3_35. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21290321 Review.
-
Ca2+ signaling, TRP channels, and endothelial permeability.Microcirculation. 2006 Dec;13(8):693-708. doi: 10.1080/10739680600930347. Microcirculation. 2006. PMID: 17085428 Review.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Transient receptor potential channels in the vasculature.Physiol Rev. 2015 Apr;95(2):645-90. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2014. Physiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25834234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of transient receptor potential channels in hypertension and metabolic vascular damage.Exp Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;101(11):1338-1344. doi: 10.1113/EP085568. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27339201 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of TRP Channels in Metabolism-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 5;25(2):692. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020692. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor‑associated macrophages activated in the tumor environment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Characterization and treatment (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Oct;65(4):100. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5688. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39239752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

