Analysis of the Promoter Regions of gga-miR-31 and Its Regulation by RA and C-jun in Chicken
- PMID: 37569891
- PMCID: PMC10420004
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241512516
Analysis of the Promoter Regions of gga-miR-31 and Its Regulation by RA and C-jun in Chicken
Abstract
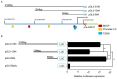
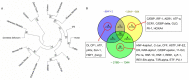
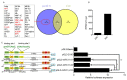
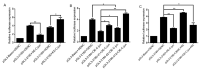
The role of gga-miR-31 in chicken germ cell differentiation and spermatogenesis is of significant importance. The transcriptional properties of gga-miR-31 are crucial in establishing the foundation for the formation of chicken spermatogonia stem cells and spermatogenesis. In this study, a series of recombinant vectors including varying lengths of the gga-miR-31 promoter were predicted and constructed. Through the utilization of the dual luciferase reporting system, the upstream -2180~0 bp region of gga-miR-31 was identified as its promoter region. Furthermore, it was predicted and confirmed that the activity of the gga-miR-31 promoter is increased by retinoic acid (RA). The binding of RA to the gga-miR-31 and Stra8 promoter regions was found to be competitive. Through the deletion of C-jun binding sites and the manipulation of C-jun expression levels, it was determined that C-jun inhibits the activity of the gga-miR-31 promoter. Furthermore, the combined treatment of C-jun and RA demonstrated that the positive regulatory effect of RA on the gga-miR-31 promoter is attenuated in the presence of high levels of C-jun. Overall, this study establishes a foundation for further investigation into the regulatory mechanisms of gga-miR-31 action, and provides a new avenue for inducing chicken embryonic stem cells (ESC) to differentiate into spermatogonial stem cells (SSC), and sperm formation.
Keywords: C-jun; RA; chicken; gga-miR-31; promoter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shao X., Gong W., Wang Q., Wang P., Shi T., Mahmut A., Qin J., Yao Y., Yan W., Chen D., et al. Atrophic skeletal muscle fibre-derived small extracellular vesicle miR-690 inhibits satellite cell differentiation during ageing. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13:3163–3180. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu B., Zhong W., Cao X., Pan G., Xu M., Zheng J., Chen H., Feng X., Luo C., Lu C., et al. Loss of miR-31-5p drives hematopoietic stem cell malignant transformation and restoration eliminates leukemia stem cells in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022;14:eabh2548. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abh2548. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu F., Liang M., Huang Y., Wu W., Zheng B., Chen C. Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal miR-31-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by negatively regulating SATB2-reversed EMT and activating MEK/ERK signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021;40:179. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01979-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

