Advances in Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Removal of Chemical Warfare Agents: Insights into Hydrolysis and Oxidation Reaction Mechanisms
- PMID: 37570496
- PMCID: PMC10420847
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13152178
Advances in Metal-Organic Frameworks for the Removal of Chemical Warfare Agents: Insights into Hydrolysis and Oxidation Reaction Mechanisms
Abstract
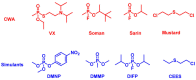
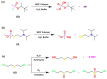
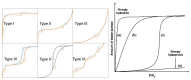
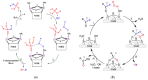
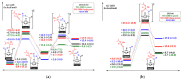
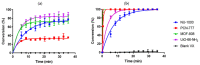
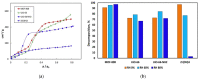
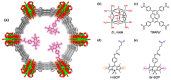
The destruction of chemical warfare agents (CWAs) is a crucial area of research due to the ongoing evolution of toxic chemicals. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), a class of porous crystalline solids, have emerged as promising materials for this purpose. Their remarkable porosity and large surface areas enable superior adsorption, reactivity, and catalytic abilities, making them ideal for capturing and decomposing target species. Moreover, the tunable networks of MOFs allow customization of their chemical functionalities, making them practicable in personal protective equipment and adjustable to dynamic environments. This review paper focuses on experimental and computational studies investigating the removal of CWAs by MOFs, specifically emphasizing the removal of nerve agents (GB, GD, and VX) via hydrolysis and sulfur mustard (HD) via selective photooxidation. Among the different MOFs, zirconium-based MOFs exhibit extraordinary structural stability and reusability, rendering them the most promising materials for the hydrolytic and photooxidative degradation of CWAs. Accordingly, this work primarily concentrates on exploring the intrinsic catalytic reaction mechanisms in Zr-MOFs through first-principles approximations, as well as the design of efficient degradation strategies in the aqueous and solid phases through the establishment of Zr-MOF structure-property relationships. Recent progress in the tuning and functionalization of MOFs is also examined, aiming to enhance practical CWA removal under realistic battlefield conditions. By providing a comprehensive overview of experimental findings and computational insights, this review paper contributes to the advancement of MOF-based strategies for the destruction of CWAs and highlights the potential of these materials to address the challenges associated with chemical warfare.
Keywords: Zr-MOFs; chemical warfare agent; computational research; degradation; hydrolysis; metal-organic framework; oxidation; reaction mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Balasubramanian S., Kulandaisamy A.J., Babu K.J., Das A., Balaguru Rayappan J.B. Metal Organic Framework Functionalized Textiles as Protective Clothing for the Detection and Detoxification of Chemical Warfare Agents—A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021;60:4218–4239. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.0c06096. - DOI
-
- Friedrich B., Hoffmann D., Renn J., Schmaltz F., Wolf M., editors. One Hundred Years of Chemical Warfare: Research, Deployment, Consequences. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. - DOI
-
- Mendonca M.L., Ray D., Cramer C.J., Snurr R.Q. Exploring the Effects of Node Topology, Connectivity, and Metal Identity on the Binding of Nerve Agents and Their Hydrolysis Products in Metal–Organic Frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2020;12:35657–35675. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c08417. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Romano J.A. Jr., Salem H., Lukey B.J., editors. Chemical Warfare Agents Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Therapeutics. 2nd ed. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2008.
-
- Wang H., Mahle J.J., Tovar T.M., Peterson G.W., Hall M.G., DeCoste J.B., Buchanan J.H., Karwacki C.J. Solid-Phase Detoxification of Chemical Warfare Agents Using Zirconium-Based Metal Organic Frameworks and the Moisture Effects: Analyze via Digestion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2019;11:21109–21116. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b04927. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

