Resveratrol Mitigates Bisphenol A-Induced Metabolic Disruptions: Insights from Experimental Studies
- PMID: 37570835
- PMCID: PMC10421514
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28155865
Resveratrol Mitigates Bisphenol A-Induced Metabolic Disruptions: Insights from Experimental Studies
Abstract
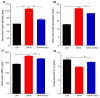
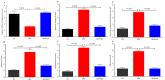
The aim of this study was to investigate the disruptions of metabolic pathways induced by bisphenol A (BPA) and explore the potential therapeutic intervention provided by resveratrol (RSV) in mitigating these disruptions through the modulation of biochemical pathways. Wistar albino rats were divided into three groups: group 1 served as the control, group 2 received 70 mg/Kg of BPA, and group 3 received 70 mg/kg of BPA along with 100 mg/Kg of RSV. After the treatment period, various biomarkers and gene expressions were measured to assess the effects of BPA and the potential protective effects of RSV. The results revealed that BPA exposure significantly increased the serum levels of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, G6PC, insulin, HbA1c, HMG-CoA reductase, FFAs, TGs, DPP-4, MDA, and proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. Concurrently, BPA exposure led to a reduction in the levels of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and superoxide dismutase (SOD), as well as GLUT4 and HDL cholesterol. However, the administration of RSV along with BPA significantly ameliorated these alterations in the biomarker levels induced through BPA exposure. RSV treatment effectively reduced the elevated levels of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, G6PC, insulin, HbA1c, HMG-CoA reductase, FFAs, TGs, DPP-4, MDA, and proinflammatory cytokines, while increasing the levels of antioxidant enzymes, GLUT4, and HDL cholesterol. Furthermore, BPA exposure suppressed the mRNA expression of glucokinase (GCK), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) and up-regulated the mRNA expression of uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2), which are all critical biomarkers involved in glucose metabolism and insulin regulation. In contrast, RSV treatment effectively restored the altered mRNA expressions of these biomarkers, indicating its potential to modulate transcriptional pathways and restore normal metabolic function. In conclusion, the findings of this study strongly suggest that RSV holds promise as a therapeutic intervention for BPA-induced metabolic disorders. By mitigating the disruptions in various metabolic pathways and modulating gene expressions related to glucose metabolism and insulin regulation, RSV shows potential in restoring normal metabolic function and counteracting the adverse effects induced by BPA exposure. However, further research is necessary to fully understand the underlying mechanisms and optimize the dosage and duration of RSV treatment for maximum therapeutic benefits.
Keywords: Glucokinase; RT-qPCR; endocrine disruptor; insulin growth factor 1; metabolic disorders; uncoupling protein 2.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest for this article.
Figures









References
-
- Akash M.S.H., Ejaz ul Haq M., Sharif H., Rehman K. Bisphenol A and Neurological Disorders: From Exposure to Preventive Interventions. In: Akash M.S.H., Rehman K., editors. Environmental Contaminants and Neurological Disorders. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switherland: 2021. pp. 185–200.
-
- Bonefeld-Jørgensen E.C., Long M., Hofmeister M.V., Vinggaard A.M. Endocrine-disrupting potential of bisphenol A, bisphenol A dimethacrylate, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-n-octylphenol in vitro: New data and a brief review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007;115((Suppl. S1)):69–76. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9368. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

