Suppression of Inflamm-Aging by Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in the Prevention of Degenerative Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence
- PMID: 37570837
- PMCID: PMC10421196
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28155867
Suppression of Inflamm-Aging by Moringa oleifera and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in the Prevention of Degenerative Diseases: A Review of Current Evidence
Abstract
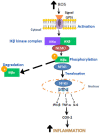
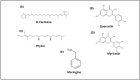
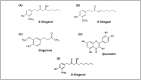
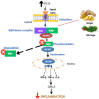
Inflammation or inflamm-aging is a chronic low-grade inflammation that contributes to numerous types of degenerative diseases among the elderly and might be impeded by introducing an anti-inflammatory agent like Moringa oleifera Lam (moringa) and Zingiber officinale Roscoe (ginger). Therefore, this paper aims to review the role of moringa and ginger in suppressing inflamm-aging to prevent degenerative diseases. Various peer-reviewed publications were searched and downloaded using the reputed search engine "Pubmed" and "Google Scholar". These materials were reviewed and tabulated. A comparison between these previous findings was made based on the mechanism of action of moringa and ginger against degenerative diseases, focusing on their anti-inflammatory properties. Many studies have reported the efficacy of moringa and ginger in type 2 diabetes mellitus, neurodegenerative disease, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and kidney disease by reducing inflammatory cytokines activities, mainly of TNF-α and IL-6. They also enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes, including catalase, glutathione, and superoxide dismutase. The anti-inflammatory activities can be seen by inhibiting NF-κβ activity. Thus, the anti-inflammatory potential of moringa and ginger in various types of degenerative diseases due to inflamm-aging has been shown in many recent types of research.
Keywords: Moringa oleifera Lam; anti-inflammatory agents; degenerative disease; inflamm-aging and Zingiber officinale Roscoe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the Anti-Hyperglycaemic, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of the Methanol Extract of Moringa Oleifera in Diabetes-Induced Nephrotoxic Male Wistar Rats.Molecules. 2017 Mar 23;22(4):439. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040439. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28333074 Free PMC article.
-
Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) for the treatment and prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 28;225:297-308. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30005955
-
The hidden mechanism beyond ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) potent in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 25;214:113-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.12.019. Epub 2017 Dec 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29253614
-
Zingiber Officinale Roscoe: The Antiarthritic Potential of a Popular Spice-Preclinical and Clinical Evidence.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 5;16(5):741. doi: 10.3390/nu16050741. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial effects of ginger Zingiber officinale Roscoe on obesity and metabolic syndrome: a review.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017 Jun;1398(1):83-98. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13375. Epub 2017 May 15. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017. PMID: 28505392 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Vistas for the Nutraceutical Withania somnifera in Inflammaging.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 7;17(5):597. doi: 10.3390/ph17050597. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Miracle Tree: Therapeutic Potential of Moringa oleifera in Chronic Disease Management and Beyond.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 5;13(3):634. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030634. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

