Phytochemistry and Biological Activities of Murraya Species
- PMID: 37570872
- PMCID: PMC10421387
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28155901
Phytochemistry and Biological Activities of Murraya Species
Abstract
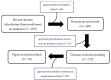
Murraya is a plant genus within the Rutaceae family comprising over 17 species, which are widely distributed in Asia, Australia, and the Pacific Islands. Furthermore, these species have been used in traditional medicine to treat fever, pain, and dysentery. Several reports have also extensively studied the leaves, seeds, stembark, and bark of Murraya from 1965 to 2023 to explore their natural product composition. Various phytochemical studies have revealed the isolation of 413 compounds recorded, comprising coumarins, terpenoids, flavonoids, and aromatics, as well as alkaloids, which constitute the largest proportion (46.9%). These isolated compounds have long been known to exhibit different bioactivities, such as cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory properties. Cytotoxic activity has been observed against HCT 116, HeLa, HepG2, and other cell lines. Previous studies have also reported the presence of antifungal, hepatoprotective, antihyperlipidemic, antidiarrheal, and antioxidant effects. Therefore, this review provides a comprehensive overview of Murraya species, highlighting their phytochemistry, biological activities, and potential as a source of active natural compounds.
Keywords: Murraya; Rutaceae; phytochemistry; secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Wilson A. Flora of Australia Volume 26 Meliaceae, Rutaceae, Zygophyllaceae. ABRS Canberra/CSIRO Publishing; Melbourne, Australia: 2013. pp. 501–503.
-
- Ma X.L., Zhu S.S., Liu Y., Chen H.W., Shi Y.T., Zeng K.W., Tu P.F. Carbazole alkaloids with potential cytotoxic activities targeted on PCK2 protein from Murraya microphylla. Bioorganic Chem. 2021;114:105–113. - PubMed
-
- Wei R., Ma Q., Zhong G., Su Y., Yang J., Wang A., Ji T., Guo H., Wang M., Jiang P., et al. Structural characterization, hepatoprotective and antihyperlipidemic activities of alkaloid derivatives from Murraya koenigii. Phytochem. Lett. 2020;35:135–140. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2019.11.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

