TM3 and STM3 Promote Flowering Together with FUL2 and MBP20, but Act Antagonistically in Inflorescence Branching in Tomato
- PMID: 37570908
- PMCID: PMC10420972
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12152754
TM3 and STM3 Promote Flowering Together with FUL2 and MBP20, but Act Antagonistically in Inflorescence Branching in Tomato
Abstract
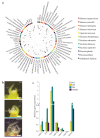
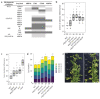
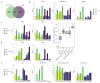
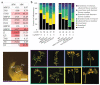
The moment at which a plant transitions to reproductive development is paramount to its life cycle and is strictly controlled by many genes. The transcription factor SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1 (SOC1) plays a central role in this process in Arabidopsis. However, the role of SOC1 in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) has been sparsely studied. Here, we investigated the function of four tomato SOC1 homologs in the floral transition and inflorescence development. We thoroughly characterized the SOC1-like clade throughout the Solanaceae and selected four tomato homologs that are dynamically expressed upon the floral transition. We show that of these homologs, TOMATO MADS 3 (TM3) and SISTER OF TM3 (STM3) promote the primary and sympodial transition to flowering, while MADS-BOX PROTEIN 23 (MBP23) and MBP18 hardly contribute to flowering initiation in the indeterminate cultivar Moneyberg. Protein-protein interaction assays and whole-transcriptome analysis during reproductive meristem development revealed that TM3 and STM3 interact and share many targets with FRUITFULL (FUL) homologs, including cytokinin regulators. Furthermore, we observed that mutating TM3/STM3 affects inflorescence development, but counteracts the inflorescence-branching phenotype of ful2 mbp20. Collectively, this indicates that TM3/STM3 promote the floral transition together with FUL2/MBP20, while these transcription factors have opposite functions in inflorescence development.
Keywords: FRUITFULL; MADS-box transcription factor; SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS 1; Solanum lycopersicum; floral transition; inflorescence architecture; reproductive meristems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Lifschitz E., Eviatar T., Rozman A., Shalit A., Goldshmidt A., Amsellem Z., Alvarez J.P., Eshed Y. The tomato FT ortholog triggers systemic signals that regulate growth and flowering and substitute for diverse environmental stimuli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:6398–6403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601620103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

