A Chromosome-Level Genome of 'Xiaobaixing' (Prunus armeniaca L.) Provides Clues to Its Domestication and Identification of Key bHLH Genes in Amygdalin Biosynthesis
- PMID: 37570910
- PMCID: PMC10421183
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12152756
A Chromosome-Level Genome of 'Xiaobaixing' (Prunus armeniaca L.) Provides Clues to Its Domestication and Identification of Key bHLH Genes in Amygdalin Biosynthesis
Abstract
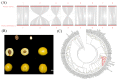
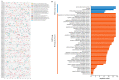
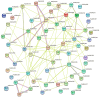
Apricot is a widely cultivated fruit tree of the drupe family, and its sweet/bitter kernel traits are important indicators of the quality and merchantability of apricots. The sweetness/bitterness traits were mainly determined by amygdalin content. However, the lack of high-quality genomes has limited insight into the traits. In this study, a high-quality genome of 'Xiaobaixing' was obtained by using single-molecule sequencing and chromosome-conformation capture techniques, with eight chromosomes of 0.21 Gb in length and 52.80% repetitive sequences. A total of 29,157 protein-coding genes were predicted with contigs N50 = 3.56 Mb and scaffold N50 = 26.73 Mb. Construction of phylogenetic trees of 15 species of Rosaceae fruit trees, with 'Xiaobaixing' differentiated by 5.3 Ma as the closest relative to 'Yinxiangbai'. GO functional annotation and KEGG enrichment analysis identified 227 specific gene families to 'Xiaobaixing', with 569 expansion-gene families and 1316 contraction-gene families, including the significant expansion of phenylalanine N-monooxygenase and β-glucosidase genes associated with amygdalin synthesis, significant contraction of wild black cherry glucoside β-glucosidase genes, amygdalin β-glucosidase genes, and β-glucosidase genes, and significant enrichment of positively selected genes in the cyanogenic amino acid metabolic pathway. The 88 bHLH genes were identified in the genome of 'Xiaobaixing', and ParbHLH66 (rna-Par24659.1) was found to be a key gene for the identification of sweet/bitter kernels of apricots. The amino acid sequence encoded by its gene is highly conserved in the species of Prunus mume, Prunus dulcis, Prunus persica, and Prunus avium and may be participating in the regulation of amygdalin biosynthesis, which provides a theoretical foundation for the molecular identification of sweet/bitter kernels of apricots.
Keywords: amygdalin; bHLH; biosynthesis; genome; xiaobaixing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Guo X. Cultivation and evaluation of Xinjiang ‘Xiaobaixing’ introduced in Chaoyang District, Liaoning Province. Spec. Econ. Anim. Plants. 2022;25:137–138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4713.2022.07.047. - DOI
-
- Hu D., Huang L., Gao J., Wang J. Research on countermeasures for high-quality development of xinjiang xiaobai apricot industry. China For. Econ. 2021;6:76–78. doi: 10.13691/j.cnki.cn23-1539/f.2021.06.019. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

