Recent Advances of Natural-Polymer-Based Hydrogels for Wound Antibacterial Therapeutics
- PMID: 37571202
- PMCID: PMC10422483
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15153305
Recent Advances of Natural-Polymer-Based Hydrogels for Wound Antibacterial Therapeutics
Abstract
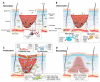
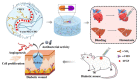
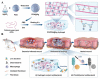
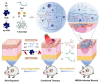
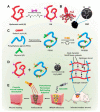
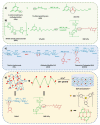
Hydrogels have a three-dimensional network structure and high-water content, are similar in structure to the extracellular matrix, and are often used as wound dressings. Natural polymers have excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability and are commonly utilized to prepare hydrogels. Natural-polymer-based hydrogels can have excellent antibacterial and bioactive properties by loading antibacterial agents or being combined with therapeutics such as phototherapy, which has great advantages in the field of treatment of microbial infections. In the published reviews of hydrogels used in the treatment of infectious wounds, the common classification criteria of hydrogels include function, source of antibacterial properties, type of antibacterial agent, etc. However, there are few reviews on the classification of hydrogels based on raw materials, and the description of natural-polymer-based hydrogels is not comprehensive and detailed. In this paper, based on the principle of material classification, the characteristics of seven types of natural polymers that can be used to prepare hydrogels are discussed, respectively, and the application of natural-polymer-based hydrogels in the treatment of infectious wounds is described in detail. Finally, the research status, limitations, and prospects of natural-polymer-based hydrogels are briefly discussed.
Keywords: antibacterial; hydrogel; natural polymer; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- BPHR202203045/the project of Cultivation for young top-notch talents of Beijing Municipal Institutions
- KM202210011002/the Beijing Municipal Education Commission project
- hc202212/the Open Research Fund Program of Cultivation Project of Double First-Class Disciplines of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Beijing Technology and Business University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

