Evaluating the Performance of Proposed Switched Beam Antenna Systems in Dynamic V2V Communication Networks
- PMID: 37571565
- PMCID: PMC10422314
- DOI: 10.3390/s23156782
Evaluating the Performance of Proposed Switched Beam Antenna Systems in Dynamic V2V Communication Networks
Abstract
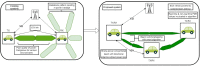
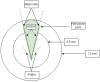
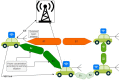
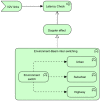
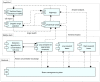
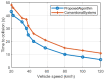
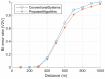
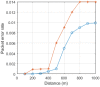
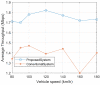
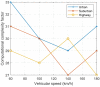
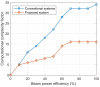
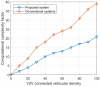
This paper develops a novel approach for reliable vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication in various environments. A switched beam antenna is deployed at the transmitting and receiving points, with a beam management system that concentrates the power in each beam using a low-computation algorithm and a potential mathematical model. The algorithm is designed to be flexible for various environments faced by vehicles. Additionally, an anti-failure system is proposed in case the intelligent transportation system (ITS) system fails to retrieve real-time Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR) values related to traffic density. Performance metrics include the time to collision in seconds, the bit error rate (BER), the packet error rate (PER), the average throughput (Mbps), the beam selection probability, and computational complexity factors. The proposed system is compared with traditional systems. Extensive experiments, simulations, and comparisons show that the proposed approach is excellent and reliable for vehicular systems. The proposed study demonstrates an average throughput of 1.7 Mbps, surpassing conventional methods' typical throughput of 1.35 Mbps. Moreover, the bit error rate (BER) of the proposed study is reduced by a factor of 0.1. Additionally, the proposed framework achieves a beam power efficiency of touching to 100% at computational factor of 34. These metrics indicate that the proposed method is both efficient and sufficiently robust.
Keywords: 5G; V2V; intelligent transportation system; vehicular safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Liu X., Liu Y., Chen Y., Hanzo L. Enhancing the fuel-economy of V2I-assisted autonomous driving: A reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020;69:8329–8342. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2996187. - DOI
-
- Gündoğan C., Kietzmann P., Lenders M.S., Petersen H., Frey M., Schmidt T.C., Shzu-Juraschek F., Wählisch M. The impact of networking protocols on massive M2M communication in the industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2021;18:4814–4828. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2021.3089549. - DOI
-
- Zhou S., Wei C., Song C., Pan X., Chang W., Yang L. Short-term traffic flow prediction of the smart city using 5G internet of vehicles based on edge computing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022;24:2229–2238. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3147845. - DOI
-
- Ahmad S.A., Hajisami A., Krishnan H., Ahmed-Zaid F., Moradi-Pari E. V2V system congestion control validation and performance. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019;68:2102–2110. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2893042. - DOI
-
- Gupta M., Benson J., Patwa F., Sandhu R. Secure V2V and V2I communication in intelligent transportation using cloudlets. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2020;15:1912–1925. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2020.3025993. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

