A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis
- PMID: 37571572
- PMCID: PMC10422350
- DOI: 10.3390/s23156790
A Wearable Multimodal Wireless Sensing System for Respiratory Monitoring and Analysis
Abstract
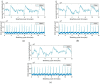
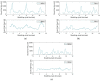
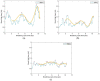
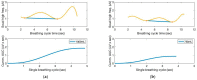
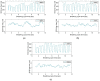
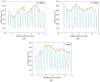
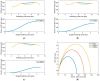
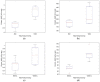
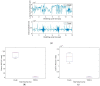
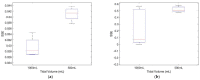
Wireless sensing systems are required for continuous health monitoring and data collection. It allows for patient data collection in real time rather than through time-consuming and expensive hospital or lab visits. This technology employs wearable sensors, signal processing, and wireless data transfer to remotely monitor patients' health. The research offers a novel approach to providing primary diagnostics remotely with a digital health system for monitoring pulmonary health status using a multimodal wireless sensor device. The technology uses a compact wearable with new integration of acoustics and biopotentials sensors to monitor cardiovascular and respiratory activity to provide comprehensive and fast health status monitoring. Furthermore, the small wearable sensor size may stick to human skin and record heart and lung activities to monitor respiratory health. This paper proposes a sensor data fusion method of lung sounds and cardiograms for potential real-time respiration pattern diagnostics, including respiratory episodes like low tidal volume and coughing. With a p-value of 0.003 for sound signals and 0.004 for electrocardiogram (ECG), preliminary tests demonstrated that it was possible to detect shallow breathing and coughing at a meaningful level.
Keywords: biomedical signal processing; digital health; medical equipment; multi-sensor fusion; respiration; wearable biomedical sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Implementation of Wearable Wireless Chest Patch Monitoring Terminal].Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2024 Sep 30;48(5):561-567. doi: 10.12455/j.issn.1671-7104.230581. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39463090 Chinese.
-
Multichannel ECG recording from waist using textile sensors.Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Jun 16;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-00788-x. Biomed Eng Online. 2020. PMID: 32546233 Free PMC article.
-
Wireless Communication Platform Based on an Embroidered Antenna-Sensor for Real-Time Breathing Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;22(22):8667. doi: 10.3390/s22228667. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433264 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in Wireless Sensors for Wearable Electronics.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Oct 9;19(20):4353. doi: 10.3390/s19204353. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31600870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wireless Technologies in Flexible and Wearable Sensing: From Materials Design, System Integration to Applications.Adv Mater. 2024 Jul;36(27):e2400333. doi: 10.1002/adma.202400333. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 38652082 Review.
Cited by
-
Multipurpose Modular Wireless Sensor for Remote Monitoring and IoT Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 17;24(4):1277. doi: 10.3390/s24041277. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38400435 Free PMC article.
-
Audio-based digital biomarkers in diagnosing and managing respiratory diseases: a systematic review and bibliometric analysis.Eur Respir Rev. 2025 May 14;34(176):240246. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0246-2024. Print 2025 Apr. Eur Respir Rev. 2025. PMID: 40368428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ming D.K., Sangkaew S., Chanh H.Q., Nhat P.T.H., Yacoub S., Georgiou P., Holmes A.H. Continuous physiological monitoring using wearable technology to inform individual management of infectious diseases, public health and outbreak responses. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020;96:648–654. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.086. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention . Asthma Facts—CDC’s National Asthma Control Program Grantees. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2013.
-
- Bellia V., Scichilone N., Battaglia S. Asthma in the elderly. Eur. Respir. Mon. 2009;43:56–76.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

