CRISPR-dependent Base Editing Screens Identify Separation of Function Mutants of RADX with Altered RAD51 Regulatory Activity
- PMID: 37572935
- PMCID: PMC10530557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168236
CRISPR-dependent Base Editing Screens Identify Separation of Function Mutants of RADX with Altered RAD51 Regulatory Activity
Abstract
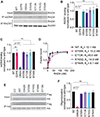
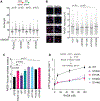
RAD51 forms nucleoprotein filaments to promote homologous recombination, replication fork reversal, and fork protection. Numerous factors regulate the stability of these filaments and improper regulation leads to genomic instability and ultimately disease including cancer. RADX is a single stranded DNA binding protein that modulates RAD51 filament stability. Here, we utilize a CRISPR-dependent base editing screen to tile mutations across RADX to delineate motifs required for RADX function. We identified separation of function mutants of RADX that bind DNA and RAD51 but have a reduced ability to stimulate its ATP hydrolysis activity. Cells expressing these RADX mutants accumulate RAD51 on chromatin, exhibit replication defects, have reduced growth, accumulate DNA damage, and are hypersensitive to DNA damage and replication stress. These results indicate that RADX must promote RAD51 ATP turnover to regulate RAD51 and genome stability during DNA replication.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA replication; Genome stability; Replication stress; single-stranded DNA binding protein.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

