Hypertonic saline induces inflammation in human macrophages through the NLRP1 inflammasome
- PMID: 37573430
- PMCID: PMC10575766
- DOI: 10.1038/s41435-023-00218-7
Hypertonic saline induces inflammation in human macrophages through the NLRP1 inflammasome
Abstract
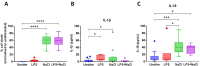
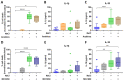
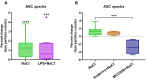
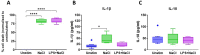
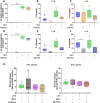
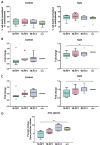
Nebulized hypertonic saline (3-7%) is commonly used to increase mucociliary clearance in patients with chronic airway disease and/or virus infections. However, altered salt concentrations may contribute to inflammatory responses. The aim of this study was to investigate whether 500 mM NaCl (3%) triggers inflammation in human macrophages and identify the molecular mechanisms involved. NaCl-induced pyroptosis, IL-1β, IL-18 and ASC speck release were measured in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages. Treatment with the recombinant IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra or the NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950 did not affect NaCl-mediated inflammasome assembly. Knock-down of NLRP1 expression, but not of NLRP3 and NLRC4, reduced NaCl-induced pyroptosis, pro-inflammatory cytokine and ASC speck release from human THP-1-derived macrophages. Data from this study suggest that 3% NaCl-induced inflammatory responses in human macrophages depend on NLRP1 and inflammasome assembly. Targeting inflammation in addition to inhalation with hypertonic saline may benefit patients with inflammatory airway disease.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ratjen F, Davis SD, Stanojevic S, Kronmal RA, Hinckley Stukovsky KD, Jorgensen N, et al. Inhaled hypertonic saline in preschool children with cystic fibrosis (SHIP): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7:802–9. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30187-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tal G, Cesar K, Oron A, Houri S, Ballin A, Mandelberg A. Hypertonic saline/epinephrine treatment in hospitalized infants with viral bronchiolitis reduces hospitalization stay: 2 years experience. Isr Med Assoc J. 2006;8:169–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

