Potential Galactagogue Effect of Tri-Than-Thip Remedy on Milk Synthesis in Lactating Rats: Impact on Milk Production-Related Parameters
- PMID: 37575273
- PMCID: PMC10416721
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.83869
Potential Galactagogue Effect of Tri-Than-Thip Remedy on Milk Synthesis in Lactating Rats: Impact on Milk Production-Related Parameters
Abstract
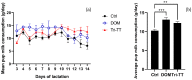
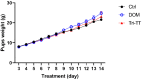
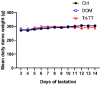
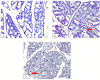
Herbal galactagogues have been widely used as a treatment for postpartum hypogalactia due to the potential side effects associated with pharmacological therapy. Tri-Than-Thip (Tri-TT) is a Thai herbal medicine remedy that contains three main components: Cassia fistula, Pithecellobium dulce, and Ficus benjamina. These components are believed to have properties that contribute to milk production. However, despite the traditional use of Tri-TT, there is a lack of academic evidence supporting its efficacy in enhancing milk production. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of Tri-TT on milk production and determine if it has a galactagogue effect. The weight suckle weight model was used to determine total milk production in lactating rats, while histological analysis was performed to assess the alveolar diameter of the mammary gland. The findings of this study revealed a significant increase in total milk production among lactating rats treated with 500 mg/kg of Tri-TT, compared to the control group. Furthermore, both the Tri-TT and Domperidone-treated groups exhibited a larger alveolar diameter of the mammary gland in comparison to the control group. In summary, these findings provide supportive evidence for the galactagogue activity of Tri-TT. The observed enhancement in milk production may be associated with Tri-TT could potentially be attributed to its ability to widen the alveolar diameter of the mammary gland, thereby facilitating increased milk volume.
Keywords: Thai herbal medicine; Tri-Than-Thip remedy; galactagogue; hypogalactia; lactating rats; milk production.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An Herbal Galactagogue Mixture Increases Milk Production and Aquaporin Protein Expression in the Mammary Glands of Lactating Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:760585. doi: 10.1155/2015/760585. Epub 2015 May 5. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26075000 Free PMC article.
-
LC-QTOF-MS Characterization, Antioxidant Activity, and In Vitro Toxicity of Medicinal Plants from the Tri-Than-Thip Remedy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 31;2022:4477003. doi: 10.1155/2022/4477003. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35140798 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a blend extract of Sauropus androgynus, Moringa oleifera, and Coleus amboinicus on milk production in lactating rats.Open Vet J. 2024 Dec;14(12):3630-3639. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i12.44. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 39927372 Free PMC article.
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast-Based Supplementation as a Galactagogue in Breastfeeding Women? A Review of Evidence from Animal and Human Studies.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 25;13(3):727. doi: 10.3390/nu13030727. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33668808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of herbals as galactagogues.J Pharm Pract. 2012 Apr;25(2):222-31. doi: 10.1177/0897190011431636. J Pharm Pract. 2012. PMID: 22392841 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo analysis of puerarin from Pueraria tuberosa as a promising galactagogue.Bioinformation. 2024 Nov 30;20(11):1574-1581. doi: 10.6026/9732063002001574. eCollection 2024. Bioinformation. 2024. PMID: 40162455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forinash AB, Yancey AM, Barnes KN, Myles TD. The use of galactogogues in the breastfeeding mother. Ann Pharmacother. 2012;46:1392–404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

