Variable Intrafamilial Expression of ABCB4 Disease
- PMID: 37575491
- PMCID: PMC10419571
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001113
Variable Intrafamilial Expression of ABCB4 Disease
Abstract
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 (PFIC3) is a rare cholestatic liver disease with autosomal recessive inheritance caused by mutations in the ABCB4 gene. The clinical presentation of PFIC3 varies significantly, displaying incomplete penetrance without clear genotype-phenotype correlations. As such, the suitability of living-related liver donation for children with advanced disease has been questioned. We report here the long-term follow-up of a patient with PFIC3 resulting in decompensated cirrhosis at 11 years who successfully underwent living donor liver transplantation from his father, who carried the same ABCB4 homozygous mutation.
Keywords: ABCB4; cholestasis; genotype; penetrance; phenotype; transplantation.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
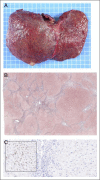
Figures


References
-
- Stättermayer AF, Halilbasic E, Wrba F, Ferenci P, Trauner M. Variants in ABCB4 (MDR3) across the spectrum of cholestatic liver diseases in adults. J Hepatol. 2020;73:651–63. - PubMed
-
- Colombo C, Vajro P, Degiorgio D, et al. Clinical features and genotype-phenotype correlations in children with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 related to ABCB4 mutations. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;52:73–83. - PubMed
-
- Davit-Spraul A, Gonzales E, Baussan C, Jacquemin E. The spectrum of liver diseases related to ABCB4 gene mutations: Pathophysiology and clinical aspects. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:134–46. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

