Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus as growing aetiologies of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37575883
- PMCID: PMC10413159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100811
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus as growing aetiologies of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
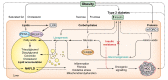
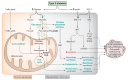
Obesity-related complications such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) are well-established risk factors for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This review provides insights into the molecular mechanisms that underlie the role of steatosis, hyperinsulinemia and hepatic inflammation in HCC development and progression. We focus on recent findings linking intracellular pathways and transcription factors that can trigger the reprogramming of hepatic cells. In addition, we highlight the role of enzymes in dysregulated metabolic activity and consequent dysfunctional signalling. Finally, we discuss the potential uses and challenges of novel therapeutic strategies to prevent and treat NAFLD/T2D-associated HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; hepatocyte transformation; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity; type 2 diabetes.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Llovet J.M., Kelley R.K., Villanueva A., Singal A.G., Pikarsky E., Roayaie S., et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7:6. - PubMed
-
- Sanyal A.J., Harrison S.A., Ratziu V., Abdelmalek M.F., Diehl A.M., Caldwell S., et al. The natural history of advanced fibrosis due to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: data from the simtuzumab trials. Hepatology. 2019;70:1913–1927. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

