Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome in childhood: a narrative review
- PMID: 37575981
- PMCID: PMC10421667
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1108345
Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome in childhood: a narrative review
Abstract
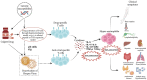
Despite being rare, the Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) syndrome is a serious, possibly fatal condition that may affect both adults and children who may be also burdened by delayed sequelae. It is an adverse drug reaction characterized by widespread skin involvement, fever, lymphadenopathy, visceral involvement, and laboratory abnormalities (eosinophilia, mononucleosis-like atypical lymphocytes). It is more frequently triggered by anticonvulsants, sulphonamides, or antibiotics, the latter being responsible for up to 30% of pediatric cases. The disease typically develops 2-8 weeks after exposure to the culprit medication, with fever and widespread skin eruption; mild viral prodromes are possible. Unfortunately, diagnosis is challenging due to the absence of a reliable test; however, a score by the European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (RegiSCAR) allows to classify suspect patients into no, possible, probable, or definite DRESS cases. Moreover, rapid-onset DRESS syndrome has been described in recent years. It affects children more often than adults and differs from the most common form because it appears ≤15 days vs. >15 days after starting the drug, it is usually triggered by antibiotics or iodinated contrast media rather than by anticonvulsants and has a higher presence of lymphadenopathy. Differential diagnosis between rapid-onset antibiotic-driven DRESS syndrome, viral exanthems, or other drug eruptions may be challenging, but it is mandatory to define it as early as possible to start adequate treatment and monitor possible complications. The present review reports the latest evidence about the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric DRESS syndrome.
Keywords: DRESS; antibiotics; anticonvulsants; children; drug hypersensitivity; drug reaction; drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.
Copyright © 2023 Manieri, Dondi, Neri and Lanari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dondi A, Parladori R, Mori F, Liccioli G, Bassi A, Lanari M, et al. Viral rashes mimicking drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms syndrome in children after β-lactams intake: a diagnostic challenge. Eur J Pediatr. (2021) 180:2327–32. doi: 10.1007/s00431-021-04010-5, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hiransuthikul A, Rattananupong T, Klaewsongkram J, Rerknimitr P, Pongprutthipan M, Ruxrungtham K. Drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome/drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DIHS/DRESS): 11 years retrospective study in Thailand. Allergol Int Off J Jpn Soc Allergol. (2016) 65:432–8. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2016.04.001, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

