A herb mixture to ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats fed a high-fat diet
- PMID: 37576314
- PMCID: PMC10415919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18889
A herb mixture to ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats fed a high-fat diet
Abstract
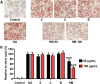
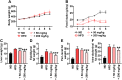
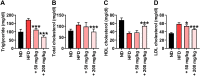
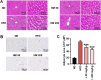
This study was performed to investigate the effects of an herb extract mixture (HM) in ameliorating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The HM contained equal amounts of 70% ethanol extracts from Zingiber officinale, Centella asiatica, and Boehmeria nivea. In vitro, the HM significantly inhibited lipid accumulation in oleic acid-stimulated HepG2 cells. We further evaluated the anti-NAFLD activities of the HM in vivo in an animal model. Rats were fed two different amounts of the HM (50 and 200 mg/kg body weight) along with a high-fat diet for 6 weeks. HM supplementation reduced liver weight; epididymal, peri-renal, and intra-abdominal fat content; and serum triglyceride, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels as well as increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in a dose-dependent manner. Histological evaluation of liver specimens further demonstrated that administration of HM significantly prevented hepatic lipid accumulation and subsequent development of hepatic steatosis. These findings suggest that HM can be used as an alternative nutraceutical for ameliorating NAFLD.
Keywords: Boehmeria nivea; Centella asiatica; Combinatorial herb extract; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Zingiber officinale.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Minaya D.M., Turlej A., Joshi A., Nagy T., Weinstein N., DiLorenzo P., Hajnal A., Czaja K. Consumption of a high energy density diet triggers microbiota dysbiosis, hepatic lipidosis, and microglia activation in the nucleus of the solitary tract in rats. Nutr. Diabetes. 2020;10:20. doi: 10.1038/s41387-020-0119-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Riazi K., Azhari H., Charette J.H., Underwood F.E., King J.A., Afshar E.E., Swain M.G., Congly S.E., Kaplan G.G., Shaheen A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

