Challenges and Opportunities in the Crusade of BRAF Inhibitors: From 2002 to 2022
- PMID: 37576670
- PMCID: PMC10413849
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00332
Challenges and Opportunities in the Crusade of BRAF Inhibitors: From 2002 to 2022
Abstract
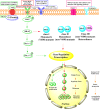
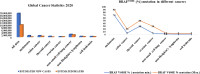
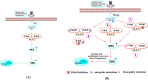
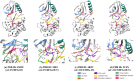
Serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf (BRAF; RAF = rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma) plays an important role in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling cascade. Somatic mutations in the BRAF gene were first discovered in 2002 by Davies et al., which was a major breakthrough in cancer research. Subsequently, three different classes of BRAF mutants have been discovered. This class includes class I monomeric mutants (BRAFV600), class II BRAF homodimer mutants (non-V600), and class III BRAF heterodimers (non-V600). Cancers caused by these include melanoma, thyroid cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, nonsmall cell lung cancer, and others. In this study, we have highlighted the major binding pockets in BRAF protein, their active and inactive conformations with inhibitors, and BRAF dimerization and its importance in paradoxical activation and BRAF mutation. We have discussed the first-, second-, and third-generation drugs approved by the Food and Drug Administration and drugs under clinical trials with all four different binding approaches with DFG-IN/OUT and αC-IN/OUT for BRAF protein. We have investigated particular aspects and difficulties with all three generations of inhibitors. Finally, this study has also covered recent developments in synthetic BRAF inhibitors (from their discovery in 2002 to 2022), their unique properties, and importance in inhibiting BRAF mutants.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

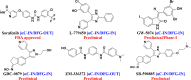
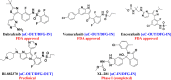
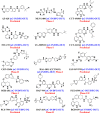
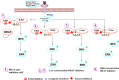





References
-
- Palmieri G.; Colombino M.; Cristina M.; Antonio P.; Lissia A.; Cossu A. Targeted therapies in melanoma: Successes and pitfalls. IntechOpen 2013, 29–58. 10.5772/53624. - DOI
-
- Palmieri G.; Rozzo C.; Gentilcore G.; Ascierto P. A.. Melanoma pathophysiology and drug targets. Futur. Med. 2012.6. 10.2217/ebo.11.29 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

