One in four patients with gastrointestinal bleeding develops shock or hemodynamic instability: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37576706
- PMCID: PMC10415974
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i28.4466
One in four patients with gastrointestinal bleeding develops shock or hemodynamic instability: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Hemodynamic instability and shock are associated with untoward outcomes in gastrointestinal bleeding. However, there are no studies in the existing literature on the proportion of patients who developed these outcomes after gastrointestinal bleeding.
Aim: To determine the pooled event rates in the available literature and specify them based on the bleeding source.
Methods: The protocol was registered on PROSPERO in advance (CRD42021283258). A systematic search was performed in three databases (PubMed, EMBASE, and CENTRAL) on 14th October 2021. Pooled proportions with 95%CI were calculated with a random-effects model. A subgroup analysis was carried out based on the time of assessment (on admission or during hospital stay). Heterogeneity was assessed by Higgins and Thompson's I2 statistics. The Joanna Briggs Institute Prevalence Critical Appraisal Tool was used for the risk of bias assessment. The Reference Citation Analysis (https://www.referencecitationanalysis.com/) tool was applied to obtain the latest highlight articles.
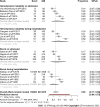
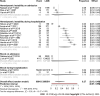
Results: We identified 11589 records, of which 220 studies were eligible for data extraction. The overall proportion of shock and hemodynamic instability in general gastrointestinal bleeding patients was 0.25 (95%CI: 0.17-0.36, I2 = 100%). In non-variceal bleeding, the proportion was 0.22 (95%CI: 0.14-0.31, I2 = 100%), whereas it was 0.25 (95%CI: 0.19-0.32, I2 = 100%) in variceal bleeding. The proportion of patients with colonic diverticular bleeding who developed shock or hemodynamic instability was 0.12 (95%CI: 0.06-0.22, I2 = 90%). The risk of bias was low, and heterogeneity was high in all analyses.
Conclusion: One in five, one in four, and one in eight patients develops shock or hemodynamic instability on admission or during hospitalization in the case of non-variceal, variceal, and colonic diverticular bleeding, respectively.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal bleeding; Hemodynamic instability; Meta-analysis; Review; Shock; Statistics.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures



References
-
- Oakland K. Changing epidemiology and etiology of upper and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol . 2019;42-43:101610. - PubMed
-
- Marmo R, Koch M, Cipolletta L, Capurso L, Pera A, Bianco MA, Rocca R, Dezi A, Fasoli R, Brunati S, Lorenzini I, Germani U, Di Matteo G, Giorgio P, Imperiali G, Minoli G, Barberani F, Boschetto S, Martorano M, Gatto G, Amuso M, Pastorelli A, Torre ES, Triossi O, Buzzi A, Cestari R, Della Casa D, Proietti M, Tanzilli A, Aragona G, Giangregorio F, Allegretta L, Tronci S, Michetti P, Romagnoli P, Nucci A, Rogai F, Piubello W, Tebaldi M, Bonfante F, Casadei A, Cortini C, Chiozzini G, Girardi L, Leoci C, Bagnalasta G, Segato S, Chianese G, Salvagnini M, Rotondano G. Predictive factors of mortality from nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: a multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol . 2008;103:1639–47; quiz 1648. - PubMed
-
- Abougergi MS, Travis AC, Saltzman JR. The in-hospital mortality rate for upper GI hemorrhage has decreased over 2 decades in the United States: a nationwide analysis. Gastrointest Endosc . 2015;81:882–8.e1. - PubMed
-
- Peery AF, Crockett SD, Murphy CC, Lund JL, Dellon ES, Williams JL, Jensen ET, Shaheen NJ, Barritt AS, Lieber SR, Kochar B, Barnes EL, Fan YC, Pate V, Galanko J, Baron TH, Sandler RS. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2018. Gastroenterology . 2019;156:254–272.e11. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

