Molecular engineering of cyclic azobenzene-peptide hybrid ligands for the purification of human blood Factor VIII via photo-affinity chromatography
- PMID: 37576949
- PMCID: PMC10421628
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202213881
Molecular engineering of cyclic azobenzene-peptide hybrid ligands for the purification of human blood Factor VIII via photo-affinity chromatography
Abstract
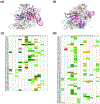
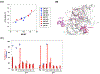
The use of benign stimuli to control the binding and release of labile biologics for their isolation from complex feedstocks is a key goal of modern biopharmaceutical technology. This study introduces cyclic azobenzene-peptide (CAP) hybrid ligands for the rapid and discrete photo-responsive capture and release of blood coagulation Factor VIII (FVIII). A predictive method - based on amino acid sequence and molecular architecture of CAPs - was developed to correlate the conformation of cis/trans CAP photo-isomers to FVIII binding and release. The combined in silico and in vitro analysis of FVIII:peptide interactions guided the design of a rational approach to optimize isomerization kinetics and biorecognition of CAPs. A photoaffinity adsorbent, prepared by conjugating selected CAP G-cycloAZOB[Lys-YYKHLYN-Lys]-G on translucent chromatographic beads, featured high binding capacity (> 6 mg of FVIII per mL of resin) and rapid photo-isomerization kinetics (τ < 30s) when exposed to 420-450 nm light at the intensity of 0.1 W·cm-2. The adsorbent purified FVIII from a recombinant harvest using a single mobile phase, affording high product yield (>90%), purity (>95%), and blood clotting activity. The CAPs introduced in this report demonstrate a novel route integrating gentle operational conditions in a rapid and efficient bioprocess for the purification of life-saving biotherapeutics.
Keywords: Factor VIII; affinity ligands; azobenzene-peptide hybrids; biomolecular recognition; photo-affinity chromatography.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure. No conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



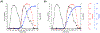
References
-
- Arora S; Saxena V; Ayyar BV, Affinity chromatography: A versatile technique for antibody purification. Methods (San Diego, Calif.) 2017, 116, 84–94. - PubMed
-
- Zhao M; Vandersluis M; Stout J; Haupts U; Sanders M; Jacquemart R, Affinity chromatography for vaccines manufacturing: Finally ready for prime time? Vaccine 2019, 37 (36), 5491–5503. - PubMed
-
- Clonis YD, Separation processes in biotechnology. Process affinity chromatography. Bioprocess technology 1990, 9, 401–45. - PubMed
-
- Chu W; Prodromou R; Day KN; Schneible JD; Bacon KB; Bowen JD; Kilgore RE; Catella CM; Moore BD; Mabe MD; Alashoor K; Xu Y; Xiao Y; Menegatti S, Peptides and pseudopeptide ligands: a powerful toolbox for the affinity purification of current and next-generation biotherapeutics. Journal of chromatography. A 2021, 1635, 461632. - PubMed
-
- Li Y; Stern D; Lock LL; Mills J; Ou SH; Morrow M; Xu X; Ghose S; Li ZJ; Cui H, Emerging biomaterials for downstream manufacturing of therapeutic proteins. Acta biomaterialia 2019, 95, 73–90. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
