Enhancement of infrared absorption through a patterned thin film of magnetic field and spin-coating directed self-assembly of gold nanoparticle stabilised ferrofluid emulsion
- PMID: 37577102
- PMCID: PMC10413183
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra01369c
Enhancement of infrared absorption through a patterned thin film of magnetic field and spin-coating directed self-assembly of gold nanoparticle stabilised ferrofluid emulsion
Abstract
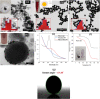
Molecular vibration signals were amplified by the gold strip gratings as a result of grating resonances and nearby electric field hotspots. Colloidal gold island films exhibit similar enhancement; however, the uneven geometrical characteristics of these films restrict the tunability of the vibrational enhancement. Infrared absorption is enhanced by regular metallic patterns such as arrays of strips fabricated using a top-down approach such as nanolithography, although this technology is expensive and difficult. The significant infrared absorption may serve as tuneable antenna sensitization to improve the sensor performance. In this article, we present a simple one-step process for fabricating optically sensitive ordered arrays of a gold nanoparticle ferrofluid emulsion in polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) using a magnetic field-directed and spin-coating self-assembly (MDSCSA) process. Techniques such as UV-visible absorption, scanning electron microscopy, and grazing-angle infrared spectroscopy were used to evaluate various parameters associated with the nanostructures. Unlike the gold strips, the chain-like features in the iron oxide nanoparticle arrays were discontinuous. The fabricated chain-like ordered arrays have been shown to increase the local field to enhance the infrared absorption corresponding to the symmetric vibration of the -CH2 (2918 cm-1) group present in PVA by ∼667% at a 45° grazing angle, as the chain thickness (CT) increased by 178%. This scalable and simple method can potentially generate low-cost patterns for antenna sensitisation.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Henares T. G. Mizutani F. Hisamoto H. Current development in microfluidic immunosensing chip. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008;611(1):17–30. - PubMed
-
- Dehghani S. Nosrati R. Yousefi M. Nezami A. Soltani F. Taghdisi S. M. Abnous K. Alibolandi M. Ramezani M. Aptamer-based biosensors and nanosensors for the detection of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018;110:23–37. - PubMed
-
- Lu Z. Yadong Y. Colloidal nanoparticle clusters: functional materials by design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012;41(21):6874–6887. - PubMed
-
- Zhijie Y. Jingjing W. Konrad G. Myung-Geun S. Bartosz G. Interference-like patterns of static magnetic fields imprinted into polymer/nanoparticle composites. Naturecomms. 2017;8(1):1–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

