Cost-effective smartphone-based method for low range chemical oxygen demand analysis
- PMID: 37577171
- PMCID: PMC10415782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102300
Cost-effective smartphone-based method for low range chemical oxygen demand analysis
Abstract
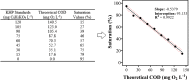
Aiming the decentralization of monitoring policies and to facilitate the work of researchers, mainly in developing countries, the present method deals with the explanation of a simple and rapid protocol for chemical oxygen demand (COD) analysis through the use of digital smartphone devices coupled with a camera and a free app available for Android operating system that recognizes HSV (hue, saturation, value). The calibration of the method is done based on the theoretical values of potassium hydrogen phthalate for a proper and reliable build of the calibration curve by using the smartphone-based technique and the digested samples of COD. The coefficient of determination (R2) attained a value upper than 0.99, providing a high confidence levels, and the method achieved 97% of average accuracy in samples with COD values ranging from 0 to 150 mg L-1. Finally, the procedure here presented can be a great support for scientific laboratories and monitoring policies, once it can efficiently substitute expensive spectrophotometers and can improve and ensure the sustainable management of water sanitation, which is one of the sustainable goals proposed by the United Nations.•COD measurements, based on the use of a simple smartphone with a camera, can be a promising way for environmental analysis when spectrophotometers are not available, such as decentralized approaches.•The use of smartphone protocol is a novel initiative to fulfill sustainable development goal 6 on clean water and sanitation.•The smartphone is capable to read the difference of HSV values efficiently and can substitute the use of expensive spectrophotometers.
Keywords: COD; Digital image colorimetry; HSV image processing; Smartphone-based method for low range chemical oxygen demand analysis; Smartphone-based technology.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- de Castro C.M., Olivi P., de Freitas Araújo K.C., Barbosa Segundo I.D., v. dos Santos E., Martínez-Huitle C.A. Environmental application of a cost-effective smartphone-based method for COD analysis: applicability in the electrochemical treatment of real wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023;855 doi: 10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.158816. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li D., Liu S. Water quality monitoring in aquaculture. Water Qual. Monit. Manag. 2019:303–328. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-811330-1.00012-0. - DOI
-
- Reed R. Waste handling in the brewing industry. Brew. New Technol. 2006:335–357. doi: 10.1533/9781845691738.335. - DOI
-
- Böck F.C., Helfer G.A., Ben da Costa A., Dessuy M.B., Ferrão M.F. PhotoMetrix and colorimetric image analysis using smartphones. J. Chemom. 2020;34 doi: 10.1002/cem.3251. - DOI
-
- Anh-Dao L.T., Thanh-Nho N., Huu-Trung B., Tien-Giang N., Ut Dong T., Quoc-Duy N., Quang-Hieu N., Le-Vy N., Thanh-Dieu N.T., To D.V.T., Minh-Huy D., Cong-Hau N. A portable colorimetric tool using a smartphone camera applied for determining total phenolic contents in coffee products. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2023;51 doi: 10.1016/j.cjac.2023.100228. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

