Roles and Molecular Mechanisms of Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Microvascular Invasion: A Review
- PMID: 37577231
- PMCID: PMC10412705
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00013S
Roles and Molecular Mechanisms of Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Microvascular Invasion: A Review
Abstract
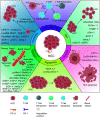
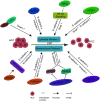
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) being a leading cause of cancer-related death, has high associated mortality and recurrence rates. It has been of great necessity and urgency to find effective HCC diagnosis and treatment measures. Studies have shown that microvascular invasion (MVI) is an independent risk factor for poor prognosis after hepatectomy. The abnormal expression of biomacromolecules such as circ-RNAs, lncRNAs, STIP1, and PD-L1 in HCC patients is strongly correlated with MVI. Deregulation of several markers mentioned in this review affects the proliferation, invasion, metastasis, EMT, and anti-apoptotic processes of HCC cells through multiple complex mechanisms. Therefore, these biomarkers may have an important clinical role and serve as promising interventional targets for HCC. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview on the functions and regulatory mechanisms of MVI-related biomarkers in HCC.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Microvascular invasion; Molecular mechanism; Progress.
© 2023 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
JWPY has been an editorial board member of Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology since 2021. The other authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
