Prognostic value of baseline and early treatment response of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein, and lactate dehydrogenase in non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing immunotherapy
- PMID: 37577328
- PMCID: PMC10413036
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-7
Prognostic value of baseline and early treatment response of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein, and lactate dehydrogenase in non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Not all non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients will benefit from immune checkpoint therapy and use of these medications carry serious autoimmune adverse effects. Therefore, biomarkers are needed to better identify patients who will benefit from its use. Here, the correlation of overall survival (OS) with baseline and early treatment period serum biomarker responses was evaluated in patients with NSCLC undergoing immunotherapy.
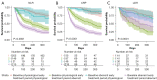
Methods: Patients diagnosed with NSCLC undergoing immunotherapy (n=597) at a tertiary academic medical center in South Korea were identified between January 2010 and November 2021. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), C-reactive protein (CRP), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels in the survival and non-survival groups were examined at baseline and early treatment periods. Additionally, aberrant laboratory parameters at each period were used to stratify survival curves and examine their correlation with one-year OS.
Results: In the non-survival group, the NLR, CRP, and LDH levels at the early treatment period were higher than those at the baseline (P<0.001). The survival curves stratified based on aberrant laboratory findings in each period varied (log-rank test P<0.001). Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that having prescribed more than 3rd line of chemotherapy [hazard ratio (HR) =3.19, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.04-9.82; P=0.043] and early treatment period CRP (HR =3.88; 95% CI: 1.55-9.72; P=0.004) and LDH (HR =4.04; 95% CI: 2.01-8.12; P<0.001) levels were significant predictors of one-year OS.
Conclusions: Early treatment period CRP and LDH levels were significant predictors of OS in patients with NSCLC undergoing immunotherapy.
Keywords: C-reactive protein (CRP); Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); immunotherapy; lactate dehydrogenase (LDH); neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR).
2023 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-7/coif). MS received funding from MD-PhD/Medical Scientist Training Program (the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea). The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Comment in
-
The role of laboratory tests as a prognostic marker for immune-checkpoint therapy in non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Sep 28;12(9):1838-1841. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-566. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37854158 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Immunotherapy: remember the host.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 26;12(12):2366-2369. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-743. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38205215 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
