Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals the regulatory effects of artesunate on splenic immune cells in polymicrobial sepsis
- PMID: 37577384
- PMCID: PMC10422109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.02.006
Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals the regulatory effects of artesunate on splenic immune cells in polymicrobial sepsis
Abstract
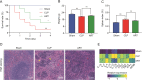
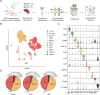
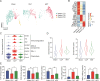
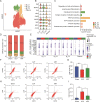
Sepsis is characterized by a severe and life-threatening host immune response to polymicrobial infection accompanied by organ dysfunction. Studies on the therapeutic effect and mechanism of immunomodulatory drugs on the sepsis-induced hyperinflammatory or immunosuppression states of various immune cells remain limited. This study aimed to investigate the protective effects and underlying mechanism of artesunate (ART) on the splenic microenvironment of cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis model mice using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and experimental validations. The scRNA-seq analysis revealed that ART inhibited the activation of pro-inflammatory macrophages recruited during sepsis. ART could restore neutrophils' chemotaxis and immune function in the septic spleen. It inhibited the activation of T regulatory cells but promoted the cytotoxic function of natural killer cells during sepsis. ART also promoted the differentiation and activity of splenic B cells in mice with sepsis. These results indicated that ART could alleviate the inflammatory and/or immunosuppressive states of various immune cells involved in sepsis to balance the immune homeostasis within the host. Overall, this study provided a comprehensive investigation of the regulatory effect of ART on the splenic microenvironment in sepsis, thus contributing to the application of ART as adjunctive therapy for the clinical treatment of sepsis.
Keywords: Artesunate; Immunomodulatory activity; Sepsis; Single-cell RNA sequencing.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

