This is a preprint.
Distinct pulmonary and systemic effects of dexamethasone in severe COVID-19
- PMID: 37577607
- PMCID: PMC10418533
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3168149/v1
Distinct pulmonary and systemic effects of dexamethasone in severe COVID-19
Update in
-
Distinct pulmonary and systemic effects of dexamethasone in severe COVID-19.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 28;15(1):5483. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49756-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38942804 Free PMC article.
Abstract
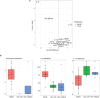
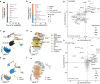
Dexamethasone is the standard of care for critically ill patients with COVID-19, but the mechanisms by which it decreases mortality and its immunological effects in this setting are not understood. We performed bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing of the lower respiratory tract and blood, and plasma cytokine profiling to study the effect of dexamethasone on systemic and pulmonary immune cells. We find decreased signatures of antigen presentation, T cell recruitment, and viral injury in patients treated with dexamethasone. We identify compartment- and cell- specific differences in the effect of dexamethasone in patients with severe COVID-19 that are reproducible in publicly available datasets. Our results highlight the importance of studying compartmentalized inflammation in critically ill patients.
Figures









References
-
- Group R. C. et al. Higher dose corticosteroids in hospitalised COVID-19 patients with hypoxia but not requiring ventilatory support (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. 2022.12.16.22283578 Preprint at 10.1101/2022.12.16.22283578 (2022). - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- P30 AR070155/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI170239/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI093615/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI168390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE032033/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL163491/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE028891/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL140026/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL151117/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI077439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

