Evaluation of Predicting Factors Affecting Sperm Retrieval in Patients with Klinefelter Syndrome: A Prospective Study
- PMID: 37577912
- PMCID: PMC10439984
- DOI: 10.22074/ijfs.2023.562534.1371
Evaluation of Predicting Factors Affecting Sperm Retrieval in Patients with Klinefelter Syndrome: A Prospective Study
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the predicting factors affecting sperm retrieval. We prospectively assessed the relationship between sonographic and microdissection testicular sperm extraction (mTESE) findings in Klinefelter syndrome (KS).
Materials and methods: In this prospective study, 44 azoospermic men with 47, XXY karyotypes participated in this study. In order to evaluate the amount of blood supply in different parts of testicular tissue, a doppler ultra-sonographic was performed. Also, for the detection of sperm in this group mTESE technique was performed.
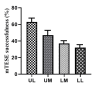
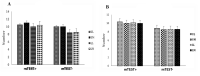
Results: The age average of positive mTESE and negative mTESE groups was 29.4 and 33.6 years, respectively. By comparing the testicle volume (based on the data obtained from the clinical examinations conducted by the urologist) it was determined that there is no significant difference between mTESE positive and negative groups. Folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) levels in men with negative mTESE (P=0.03) and testosterone levels in men with positive mTESE significantly increased (P=0.017). The overall rate of testis vascularity was significantly higher in the positive mTESE group than in the negative mTESE group. The clinical pregnancy rate in positive mTESE men was 9% per cycle, 16.6% per embryos were transferred (ET), and 12.5% per cycle.
Conclusion: Totally, our observation indicated that there is not a significant relationship between sonographic and mTESE results in KS patients. However, more investigations with bigger sample Size can be useful to validate our results.
Keywords: Azoospermic; Klinefelter; Testicular Sperm Extraction; Ultrasonography.
Figures
References
-
- Aliakbari F, Taghizabet N, Azizi F, Rezaei-Tazangi F, Gelehkolaee KS, Kharazinejad E. A review of methods for preserving male fertility. Zygote. 2022;30(3):289–97. - PubMed
-
- Corona G, Pizzocaro A, Lanfranco F, Garolla A, Pelliccione F, Vignozzi L, et al. Sperm recovery and ICSI outcomes in Klinefelter syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2017;23(3):265–275. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
