Epilepsy-associated SCN2A (NaV1.2) variants exhibit diverse and complex functional properties
- PMID: 37578743
- PMCID: PMC10424433
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.202313375
Epilepsy-associated SCN2A (NaV1.2) variants exhibit diverse and complex functional properties
Abstract
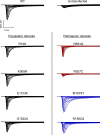
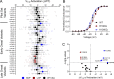
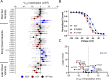
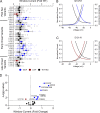
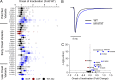
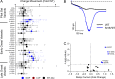
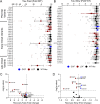
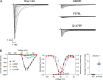
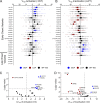
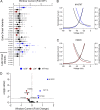
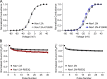
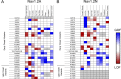
Pathogenic variants in voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channel genes including SCN2A, encoding NaV1.2, are discovered frequently in neurodevelopmental disorders with or without epilepsy. SCN2A is also a high-confidence risk gene for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and nonsyndromic intellectual disability (ID). Previous work to determine the functional consequences of SCN2A variants yielded a paradigm in which predominantly gain-of-function variants cause neonatal-onset epilepsy, whereas loss-of-function variants are associated with ASD and ID. However, this framework was derived from a limited number of studies conducted under heterogeneous experimental conditions, whereas most disease-associated SCN2A variants have not been functionally annotated. We determined the functional properties of SCN2A variants using automated patch-clamp recording to demonstrate the validity of this method and to examine whether a binary classification of variant dysfunction is evident in a larger cohort studied under uniform conditions. We studied 28 disease-associated variants and 4 common variants using two alternatively spliced isoforms of NaV1.2 expressed in HEK293T cells. Automated patch-clamp recording provided a valid high throughput method to ascertain detailed functional properties of NaV1.2 variants with concordant findings for variants that were previously studied using manual patch clamp. Many epilepsy-associated variants in our study exhibited complex patterns of gain- and loss-of-functions that are difficult to classify by a simple binary scheme. The higher throughput achievable with automated patch clamp enables study of variants with greater standardization of recording conditions, freedom from operator bias, and enhanced experimental rigor. This approach offers an enhanced ability to discern relationships between channel dysfunction and neurodevelopmental disorders.
© 2023 Thompson et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: J.J. Millichap reported personal fees from Xenon, Praxis, and Biohaven outside the submitted work. A.L. George, Jr. reported grants from Praxis Precision Medicines and Neurocrine Biosciences during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures










Update of
-
Epilepsy-associated SCN2A (Na V 1.2) Variants Exhibit Diverse and Complex Functional Properties.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 23:2023.02.23.529757. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.23.529757. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Gen Physiol. 2023 Oct 2;155(10):e202313375. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202313375. PMID: 36865317 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
No Pain, No Gain of Function: Epilepsy-Associated Variants in SCN2A Defy Classification.Epilepsy Curr. 2024 Jan 17;24(2):126-128. doi: 10.1177/15357597231225565. eCollection 2024 Mar-Apr. Epilepsy Curr. 2024. PMID: 39280051 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Begemann, A., Acuña M.A., Zweier M., Vincent M., Steindl K., Bachmann-Gagescu R., Hackenberg A., Abela L., Plecko B., Kroell-Seger J., et al. 2019. Further corroboration of distinct functional features in SCN2A variants causing intellectual disability or epileptic phenotypes. Mol. Med. 25:6. 10.1186/s10020-019-0073-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shalom, R., Keeshen C.M., Berrios K.N., An J.Y., Sanders S.J., and Bender K.J.. 2017. Opposing effects on NaV1.2 function underlie differences between SCN2A variants observed in individuals with autism spectrum disorder or infantile seizures. Biol. Psychiatry. 82:224–232. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.01.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shalom, R., Ladd A., Artherya N.S., Cross C., Kim K.G., Sanghevi H., Korngreen A., Bouchard K.E., and Bender K.J.. 2022. NeuroGPU: Accelerating multi-compartment, biophysically detailed neuron simulations on GPUs. J. Neurosci. Methods. 366:109400. 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2021.109400 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berecki, G., Howell K.B., Deerasooriya Y.H., Cilio M.R., Oliva M.K., Kaplan D., Scheffer I.E., Berkovic S.F., and Petrou S.. 2018. Dynamic action potential clamp predicts functional separation in mild familial and severe de novo forms of SCN2A epilepsy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 115:E5516–E5525. 10.1073/pnas.1800077115 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

