What Factors Explain Low Adoption of Digital Technologies for Health Financing in an Insurance Setting? Novel Evidence From a Quantitative Panel Study on IMIS in Tanzania
- PMID: 37579470
- PMCID: PMC10125074
- DOI: 10.34172/ijhpm.2023.6896
What Factors Explain Low Adoption of Digital Technologies for Health Financing in an Insurance Setting? Novel Evidence From a Quantitative Panel Study on IMIS in Tanzania
Abstract
Background: Digital information management systems for health financing are implemented on the assumption thatdigitalization, among other things, enables strategic purchasing. However, little is known about the extent to which thesesystems are adopted as planned to achieve desired results. This study assesses the levels of, and the factors associated withthe adoption of the Insurance Management Information System (IMIS) by healthcare providers in Tanzania.
Methods: Combining multiple data sources, we estimated IMIS adoption levels for 365 first-line health facilities in2017 by comparing IMIS claim data (verified claims) with the number of expected claims. We defined adoption as abinary outcome capturing underreporting (verified<expected) vs. not-underreporting, using four different approaches.We used descriptive statistics and analysis of variance (ANOVA) to examine adoption levels across facilities, districts,regions, and months. We used logistic regression to identify facility-specific factors (ie, explanatory variables) associatedwith different adoption levels.
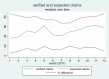
Results: We found a median (interquartile range [IQR]) difference of 77.8% (32.7-100) between expected and verifiedclaims, showing a consistent pattern of underreporting across districts, regions, and months. Levels of underreportingvaried across regions (ANOVA: F=7.24, P<.001) and districts (ANOVA: F=4.65, P<.001). Logistic regression resultsshowed that higher service volume, share of people insured, and greater distance to district headquarter were associatedwith a higher probability of underreporting.
Conclusion: Our study shows that the adoption of IMIS in Tanzania may be sub-optimal and far from policy-makers'expectations, limiting its capacity to provide the necessary information to enhance strategic purchasing in the healthsector. Countries and agencies adopting digital interventions such as openIMIS to foster health financing reform areadvised to closely track their implementation efforts to make sure the data they rely on is accurate. Further, our studysuggests organizational and infrastructural barriers beyond the software itself hamper effective adoption.
Keywords: Adoption; Digital Health Intervention; Health Financing; Health Insurance; Strategic Purchasing; Tanzania.
© 2023 The Author(s); Published by Kerman University of Medical Sciences This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Conflict of interest statement
MDA and NK declare no competing interests. SS and MS are part of the Swiss TPH project team that is implementing HPSS project under which openIMIS was implemented. ER is a project advisor for HPSS project. LS has a doctoral student agreement with and received travel support by Swiss TPH. AM has performed paid activities with HPSS project in the past.
Similar articles
-
Factors Affecting the Successful Implementation of a Digital Intervention for Health Financing in a Low-Resource Setting at Scale: Semistructured Interview Study With Health Care Workers and Management Staff.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jan 6;25:e38818. doi: 10.2196/38818. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36607708 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Digital Strategies in Financing Health Care for Universal Health Coverage in Low- and Middle-Income Countries.Glob Health Sci Pract. 2018 Oct 10;6(Suppl 1):S29-S40. doi: 10.9745/GHSP-D-18-00271. Print 2018 Oct 10. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2018. PMID: 30305337 Free PMC article.
-
Governance factors that affect the implementation of health financing reforms in Tanzania: an exploratory study of stakeholders' perspectives.BMJ Glob Health. 2021 Aug;6(8):e005964. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2021-005964. BMJ Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34413077 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing variation in implementation outcomes of the redesigned community health fund in the Dodoma region of Tanzania: a mixed-methods study.BMC Public Health. 2021 Jan 2;21(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-10013-y. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33388037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions and challenges of healthcare financing towards universal health coverage in Ethiopia: a narrative evidence synthesis.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Jul 5;22(1):866. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08151-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 35790986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Achieving universal health coverage in low- and middle-income countries through digital antimicrobial stewardship.Front Digit Health. 2023 Dec 15;5:1298861. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2023.1298861. eCollection 2023. Front Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 38162693 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Factors Affecting the Successful Implementation of a Digital Intervention for Health Financing in a Low-Resource Setting at Scale: Semistructured Interview Study With Health Care Workers and Management Staff.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jan 6;25:e38818. doi: 10.2196/38818. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36607708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Honda A. What is Strategic Purchasing for Health? RESYST; 2014. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/57a089c8e5274a27b2000271/....
-
- Figueras J, Robinson R, Jakubowski E. Purchasing to Improve Health Systems Performance. McGraw-Hill Education (UK); 2005.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources