Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide for Diabetic Macular Edema and Macular Edema Secondary to Retinal Vein Occlusion: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37579730
- PMCID: PMC10836924
- DOI: 10.1159/000533443
Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide for Diabetic Macular Edema and Macular Edema Secondary to Retinal Vein Occlusion: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The comparative safety and efficacy of different doses of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA) for diabetic macular edema (DME) and macular edema (ME) secondary to retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is unclear.
Objectives: This meta-analysis aimed to compare the safety and efficacy of different doses of IVTA in this setting.
Methods: A systematic literature search for randomized clinical trials (RCTs) was conducted on Cochrane Library, Ovid MEDLINE, and EMBASE from January 2005 to May 2022. Studies that reported on patients with DME or ME secondary to RVO that received treatment with different doses of IVTA were included. A random-effects meta-analysis was performed. Cochrane's Risk of Bias Tool 2 was used to assess the risk of bias, and Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) guidelines were used to assess certainty of evidence.
Results: Five RCTs reporting on 1,041 eyes at baseline were included in this meta-analysis. In eyes with ME secondary to RVO, high-dose (4 mg) IVTA achieved a significantly better change in best-corrected visual acuity (WMD = -4.75 ETDRS letters, 95% CI = [-7.73, -1.78], p = 0.002) and reduction in retinal thickness (WMD = -93.02 μm, 95% CI = [-153.23, -32.82], p = 0.002) at months 4-6 compared to low-dose (1-2 mg) IVTA. However, high-dose IVTA had a higher risk of intraocular pressure-related adverse events (RR = 2.99, 95% CI = [1.05, 8.50], p = 0.04) and cataract surgery (RR = 5.67, 95% CI = [3.09, 10.41], p < 0.00001) than low-dose IVTA in eyes with ME secondary to RVO. These efficacy and safety differences in high-dose and low-dose IVTA were not observed in DME eyes.
Conclusions: The RCT evidence in this setting is limited. High-dose IVTA achieved greater improvements in visual acuity and reductions in retinal thickness than low-dose IVTA at months 4-6. However, high-dose IVTA had a less favorable safety profile than low-dose IVTA. The significance of these outcomes was based on patients with ME secondary to RVO, but not DME.
Keywords: Diabetic macular edema; Retinal vein occlusion; Triamcinolone acetonide.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M., A.H., N.S.P., and M.C.P. have no conflicts of interest to declare. M.M.P.: Financial support (to institution) – PSI Foundation, Fighting Blindness Canada. P.J.K.: Advisory board – Novartis, Alcon, Bayer, Roche, Allergan, Novelty Nobility; Financial support (to institution) – Bayer, Roche, Novartis; Financial support – Novartis, Bayer, Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Zeiss; Equity owner – ArcticDx. R.H.M.: Advisory board- Alcon, Bausch + Lomb, Bayer, Novartis, Allergan, Roche; Financial Support (to institution)- Bayer, Novartis, Roche.
Figures

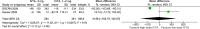
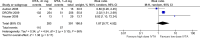



References
-
- Sutter FKP, Simpson JM, Gillies MC. Intravitreal triamcinolone for diabetic macular edema that persists after laser treatment: three-month efficacy and safety results of a prospective, randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Ophthalmology. 2004 Nov;111(11):2044–9. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.05.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ghoraba HH, Leila M, Elgouhary SM, Elgemai EEM, Abdelfattah HM, Ghoraba HH, et al. Safety of high-dose intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide as low-cost alternative to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents in lower-middleincome countries. Clin Ophthalmol. 2018 Nov 26;12:2383–2391. 10.2147/opth.s185274. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

