HSPA12A controls cerebral lactate homeostasis to maintain hippocampal neurogenesis and mood stabilization
- PMID: 37580315
- PMCID: PMC10425330
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-023-02573-5
HSPA12A controls cerebral lactate homeostasis to maintain hippocampal neurogenesis and mood stabilization
Abstract
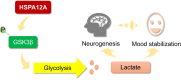
Mood instability, a subjective emotional state defined as rapid mood oscillations of up and down, is a symptom that occurs in several psychiatric disorders, particularly major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder. Heat shock protein A12A (HSPA12A) shows decreased expression in the brains of schizophrenia patients. However, the causal effects of HSPA12A in any psychiatric disorders are completely unknown. To investigate whether HSPA12A affects mood stability, Hspa12a-knockout mice (Hspa12a-/-) and wild-type (WT) littermates were subjected to tests of open field, forced swimming, elevated plus maze, and sucrose preference. Cerebral lactate levels were measured in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) was assessed by BrdU labeling. We found that acute mood stress increased hippocampal HSPA12A expression and CSF lactate levels in mice. However, Hspa12a-/- mice exhibited behaviors of mood instability (anhedonia, lower locomotor activity, antidepression, and anxiety), which were accompanied by impaired AHN, decreased CSF lactate levels, and downregulated hippocampal glycolytic enzyme expression. By contrast, HSPA12A overexpression increased lactate production and glycolytic enzyme expression of primary hippocampal neurons. Intriguingly, lactate administration alleviated the mood instability and AHN impairment in Hspa12a-/- mice. Further analyses revealed that HSPA12A was necessary for sustaining cerebral lactate homeostasis, which could be mediated by inhibiting GSK3β in hippocampal neurons, to maintain AHN and mood stabilization. Taken together, HSPA12A is defined as a novel regulator of mood stability and exerts therapeutic potential for mood disorder. Our findings establish a framework for determining mood disorder and AHN relevance of cerebral lactate homeostasis. HSPA12A is a novel mood stabilizer through inhibiting GSK3β in hippocampal neurons, thereby sustaining glycolysis-generated lactate to maintain cerebral lactate homeostasis, which ultimately leading to maintenance of hippocampal neurogenesis and mood stabilization.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ward J, Tunbridge E, Sandor C, Lyall L, Ferguson A, Strawbridge R, et al. The genomic basis of mood instability: identification of 46 loci in 363,705 UK Biobank participants, genetic correlation with psychiatric disorders, and association with gene expression and function. Mol Psych. 2020;25:3091–9. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0439-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ward J, Strawbridge R, Bailey M, Graham N, Ferguson A, Lyall D, et al. Genome-wide analysis in UK Biobank identifies four loci associated with mood instability and genetic correlation with major depressive disorder, anxiety disorder and schizophrenia. Transl Psych. 2017;7:1264. doi: 10.1038/s41398-017-0012-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stanislaus S, Faurholt-Jepsen M, Vinberg M, Coello K, Kjærstad H, Melbye S, et al. Mood instability in patients with newly diagnosed bipolar disorder, unaffected relatives, and healthy control individuals measured daily using smartphones. J Affect Disord. 2020;271:336–44.. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.03.049. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

