Sprague Dawley rats from different vendors vary in the modulation of prepulse inhibition of startle (PPI) by dopamine, acetylcholine, and glutamate drugs
- PMID: 37580441
- PMCID: PMC10471717
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-023-06444-1
Sprague Dawley rats from different vendors vary in the modulation of prepulse inhibition of startle (PPI) by dopamine, acetylcholine, and glutamate drugs
Abstract
Rationale: Rodent vendors are often utilized interchangeably, assuming that the phenotype of a given strain remains standardized between colonies. Several studies, however, have found significant behavioral and physiological differences between Sprague Dawley (SD) rats from separate vendors. Prepulse inhibition of startle (PPI), a form of sensorimotor gating in which a low-intensity leading stimulus reduces the startle response to a subsequent stimulus, may also vary by vendor. Differences in PPI between rat strains are well known, but divergence between colonies within the SD strain lacks thorough examination.
Objectives: We explored intrastrain variation in PPI by testing SD rats from two vendors: Envigo and Charles River (CR).
Methods: We selected drugs acting on four major neurotransmitter systems that have been repeatedly shown to modulate PPI: dopamine (apomorphine; 0.5, 1.5, 3.0 mg/kg), acetylcholine (scopolamine; 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 mg/kg), glutamate (dizocilpine; 0.5, 1.5, 2.5 mg/kg), and serotonin (2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine, DOI; 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mg/kg). We determined PPI and startle amplitude for each drug in male and female Envigo and CR SD rats.
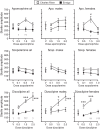
Results: SD rats from Envigo showed dose-dependent decreases in PPI after apomorphine, scopolamine, or dizocilpine administration, without significant effects on startle amplitude. SD rats from CR were less sensitive to modulation of PPI and/or more sensitive to modulation of startle amplitude, across the three drugs.
Conclusions: SD rats showed vendor differences in sensitivity to pharmacological modulation of PPI and startle. We encourage researchers to sample rats from separate vendors before experimentation to identify the most suited source of subjects for their specific endpoints.
Keywords: Acetylcholine; Dopamine; Glutamate; PPI; Prepulse inhibition; Serotonin; Sprague Dawley rats; Startle amplitude; Startle response.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA. Clozapine antagonizes phencyclidine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating of the startle response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;271:787–794. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick CJ, Gopalakrishnan S, Cogan ES, Yager LM, Meyer PJ, Lovic V, Saunders BT, Parker CC, Gonzales NM, Aryee E, Flagel SB, Palmer AA, Robinson TE, Morrow JD. Variation in the form of Pavlovian conditioned approach behavior among outbred male Sprague-Dawley rats from different vendors and colonies: sign-tracking vs. goal-tracking. PLoS One. 2013;8:e75042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

