Cerebellar deep brain stimulation for chronic post-stroke motor rehabilitation: a phase I trial
- PMID: 37580534
- PMCID: PMC10504081
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-023-02507-0
Cerebellar deep brain stimulation for chronic post-stroke motor rehabilitation: a phase I trial
Abstract
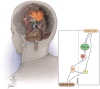
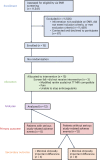
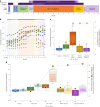
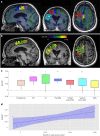
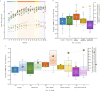
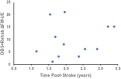
Upper-extremity impairment after stroke remains a major therapeutic challenge and a target of neuromodulation treatment efforts. In this open-label, non-randomized phase I trial, we applied deep brain stimulation to the cerebellar dentate nucleus combined with renewed physical rehabilitation to promote functional reorganization of ipsilesional cortex in 12 individuals with persistent (1-3 years), moderate-to-severe upper-extremity impairment. No serious perioperative or stimulation-related adverse events were encountered, with participants demonstrating a seven-point median improvement on the Upper-Extremity Fugl-Meyer Assessment. All individuals who enrolled with partial preservation of distal motor function exceeded minimal clinically important difference regardless of time since stroke, with a median improvement of 15 Upper-Extremity Fugl-Meyer Assessment points. These robust functional gains were directly correlated with cortical reorganization evidenced by increased ipsilesional metabolism. Our findings support the safety and feasibility of deep brain stimulation to the cerebellar dentate nucleus as a promising tool for modulation of late-stage neuroplasticity for functional recovery and the need for larger clinical trials. ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT02835443 .
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.G.M. serves as Chief Medical Officer and Chair of the Scientific Advisory Board for Enspire DBS Therapy and is paid with stock options. As the inventor, A.G.M. will receive portions of commercialization and/or Cleveland Clinic Foundation stock revenue and payments through Cleveland Clinic Foundation with fees deducted. B.H. serves as a paid member of the DMC for the corresponding phase I/II study (RESTORE). S.L.W. serves as a member of the Scientific Advisory Board and is a paid consultant to Enspire DBS Therapy. J.C. also serves as a paid consultant, but the agreement is with MetroHealth, and J.C. is their designated representative. J.C. is also a member of the Scientific Advisory Board. K.B. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board and is paid with stock options. In addition, A.B.R. is a paid consultant to Enspire DBS Therapy. Enspire DBS Therapy partially sponsored the study and had access to the safety, feasibility and secondary outcome measures. The company had no role in the drafting or editing of this manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

