Comprehensive analysis of UBE2C expression and its potential roles and mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37580802
- PMCID: PMC10457065
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204792
Comprehensive analysis of UBE2C expression and its potential roles and mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
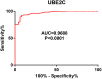
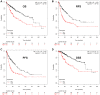
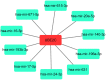
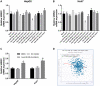
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks one of the most common and lethal cancers all over the world. Previous studies suggest that ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C (UBE2C) serves as an oncogene in human cancers. However, its expression, diagnosis, prognosis and potential mechanisms in HCC remain largely unknown. In this study, the expression of UBE2C in HCC was first analyzed by comprehensive bioinformatic analysis. ROC curve analysis and survival analysis were employed to assess the diagnostic and prognostic roles of UBE2C in HCC. UBE2C promoter methylation level and upstream regulatory miRNAs of UBE2C in HCC were explored. The present work demonstrated that UBE2C was significantly upregulated in HCC compared with normal controls. We also found significant diagnostic and prognostic values of UBE2C in HCC. Promoter methylation of UBE2C was obviously decreased in HCC and was negatively correlated with UBE2C mRNA expression. 10 miRNAs were predicted to potentially bind to UBE2C. In vitro assay and bioinformatic correlation analysis together revealed that hsa-miR-193b-3p might be another key upstream regulatory mechanism of UBE2C in HCC. In conclusion, UBE2C is overexpressed in HCC and may serve as a key diagnostic/prognostic biomarker for patients with HCC.
Keywords: UBE2C; diagnosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver cancer; microRNA (miRNA); prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

