Quantification of membrane-bound cytokine receptors by calibrated flow cytometry
- PMID: 37581983
- PMCID: PMC10457439
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102511
Quantification of membrane-bound cytokine receptors by calibrated flow cytometry
Abstract
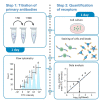
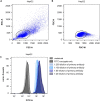
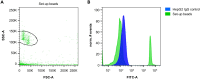
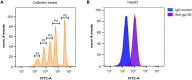
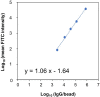
We present a protocol for quantifying the expression of the receptor gp130 using a calibrated flow cytometric approach. We describe pitfalls for receptor quantification such as titration of primary antibodies and standardizing cell culture. Receptors are stained with primary antibodies and fluorophore-coupled secondary antibodies. Beads covered with defined numbers of immunoglobulin G stained with fluorophore-coupled secondary antibodies serve as calibrators. In this way, the fluorescence intensity of cells is converted to the number of receptors on the cell surface. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Reeh et al. (2019).1.
Keywords: Flow Cytometry/Mass Cytometry; Signal Transduction; Single Cell.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Reeh H., Rudolph N., Billing U., Christen H., Streif S., Bullinger E., Schliemann-Bullinger M., Findeisen R., Schaper F., Huber H.J., Dittrich A. Response to IL-6 trans- and IL-6 classic signalling is determined by the ratio of the IL-6 receptor alpha to gp130 expression: fusing experimental insights and dynamic modelling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019;17:46. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0356-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pietzko D., Zohlnhöfer D., Graeve L., Fleischer D., Stoyan T., Schooltink H., Rose-John S., Heinrich P.C. The hepatic interleukin-6 receptor. Studies on its structure and regulation by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-dexamethasone. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:4250–4258. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53603-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

