Novel competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of the high-risk Human Papillomavirus 18 E6 oncoprotein
- PMID: 37582106
- PMCID: PMC10426986
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290088
Novel competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of the high-risk Human Papillomavirus 18 E6 oncoprotein
Abstract
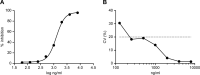
Cervical cancer represents a global concern with 604,000 new cases and 342,000 deaths reported annually, with the vast majority diagnosed in low income countries. Despite high-risk Human Papillomavirus (HR HPV)-induced cervical cancer has become highly preventable through prophylactic vaccines, screening programs are critical in the control of cervical carcinogenesis in populations with limited access to vaccination and in older generations of women who have already been exposed to HR HPV infection. The surge of HPV molecular tests has provided a more sensitive and accurate diagnostic alternative to cytology screening. Given that HPV DNA testing presents a low positive predicted value, leading to unnecessary treatment, the E6 oncoprotein from HR HPV types arises as a promising diagnostic marker for its overexpression in transformed HPV-positive cancer cells. For these reasons, this study aimed at obtaining monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against the E6 oncoprotein of one of the most prevalent HR HPV types worldwide, HPV18, in order to develop a highly specific and sensitive indirect competitive ELISA (icELISA). The production of hybridomas secreting HPV18 E6 mAbs was carried out through a combined tolerization and immunization strategy, in order to avoid cross-reactivity with the E6 protein from low-risk HPV types 6 and 11. We selected the 7D2 hybridoma clone, which recognized HPV18 E6 and showed some cross-reactivity against the HR HPV45 E6 oncoprotein. The 7D2 mAb enabled the development of a sensitive, reliable and reproducible icELISA to detect and quantify small amounts of HPV18 E6 biomarker for cervical cancer progression. The present study establishes a valid 7D2-based icELISA that constitutes a promising bioanalytical method for the early detection and quantification of HPV18 E6 oncoprotein in cervical swab samples and cancer prevention.
Copyright: © 2023 Contreras et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- IARC. Cervical cancer screening. IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention. https://publications.iarc.fr/6042022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

