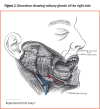
Approach to sialadenitis
- PMID: 37582587
- PMCID: PMC10426371
- DOI: 10.46747/cfp.6908531
Approach to sialadenitis
Abstract
Objective: To provide family physicians with a practical evidence-based approach to the management of patients with sialadenitis.
Sources of information: MEDLINE and PubMed databases were searched for English-language research on sialadenitis and other salivary gland disorders, as well as for relevant review articles and guidelines published between 1981 and 2021.
Main message: Sialadenitis refers to inflammation or infection of the salivary glands and is a condition that can be caused by a broad range of processes including infectious, obstructive, and autoimmune. History and physical examination play important roles in directing management, while imaging is often useful to establish a diagnosis. Red flags such as suspected abscess formation, signs of respiratory obstruction, facial paresis, and fixation of a mass to underlying tissue should prompt urgent referral to head and neck surgery or a visit to the emergency department.
Conclusion: Family physicians can play an important role in the diagnosis and management of sialadenitis. Prompt recognition and treatment of the condition can prevent the development of complications.
Copyright © 2023 the College of Family Physicians of Canada.
Figures
References
-
- Rice DH. Nonneoplastic diseases of the salivary glands. In: Bailey BJ, Johnson JT, Newlands SD, editors. Head & neck surgery—otolaryngology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006. p. 545-54.
-
- Speight PM, Barrett AW.. Salivary gland tumours. Oral Dis 2002;8(5):229-40. - PubMed
-
- Myers EN, Ferris RL, editors. Salivary gland disorders. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 2007.
-
- Arduino PG, Carrozzo M, Pentenero M, Bertolusso G, Gandolfo S.. Non-neoplastic salivary gland diseases [article in English, Italian]. Minerva Stomatol 2006;55(5):249-70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials