Study on the daily dose and serum concentration of clozapine in psychiatric patients and possible influencing factors of serum concentration
- PMID: 37582705
- PMCID: PMC10428656
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-023-05078-z
Study on the daily dose and serum concentration of clozapine in psychiatric patients and possible influencing factors of serum concentration
Abstract
Background: Clozapine is the most effective drug for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, and the dosage and concentration of clozapine in the treatment of mental illness vary greatly in different populations and are affected by many factors.
Methods: The serum clozapine concentration of 3734 psychiatric patients was detected, and data on daily dose, sex, age and other medical records were collected for statistical analysis.
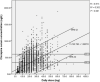
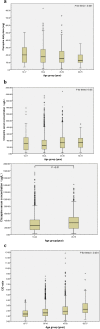
Results: The mean daily dose, mean serum concentration and mean C/D (concentration/dose) ratio of clozapine were 191.02 ± 113.47 mg/day, 326.15 ± 235.66 ng/mL and 1.94 ± 1.25 ng/mL per mg/day, respectively. There was difference in daily dose between sexes, and females had higher daily dose (p <0.01), higher serum clozapine concentrations (p < 0.01) and higher C/D ratios (p < 0.01). There were significant differences in daily dose (p < 0.001), serum drug concentration (p < 0.001) and C/D ratio (p < 0.001) among different age groups. The daily dose decreased with age (p for trend < 0.001), and the C/D ratio increased with age (p for trend < 0.001). Inpatients and outpatients had no difference in daily dose, but inpatients had higher serum concentration (p < 0.001) and C/D ratio (p < 0.001). There was no difference in daily dose among different occupations, but there were significant differences in serum concentration (p < 0.001) and C/D ratio (p < 0.001), and unemployed patients may have higher serum concentration and C/D ratio. Duration of disease, comorbidity, marital status, and psychotic type may influence the daily dose and serum concentration.
Conclusions: The effective daily dose and serum concentration of clozapine in the study area may be lower than recommended levels, and women have higher serum concentrations and slower metabolic rates. With increasing age, the daily dose decreases, and the metabolic rate slows. Inpatient status and occupation of patients may influence the serum concentration and metabolic rate of clozapine.
Keywords: Clozapine; Daily dose; Serum concentration; Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM).
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between clozapine dose, serum concentration, and clinical outcome in children and adolescents in clinical practice.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016 Aug;123(8):1021-31. doi: 10.1007/s00702-016-1573-y. Epub 2016 May 24. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016. PMID: 27221285
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring of clozapine and relapse--a retrospective study of routine clinical data.Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Jan;41(1):3-13. doi: 10.5414/cpp41003. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12564740
-
Do Indian patients with schizophrenia need half the recommended clozapine dose to achieve therapeutic serum level? An exploratory study.Schizophr Res. 2020 Aug;222:195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2020.05.057. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Schizophr Res. 2020. PMID: 32518001
-
Using therapeutic drug monitoring to personalize clozapine dosing in Asians.Asia Pac Psychiatry. 2020 Jun;12(2):e12384. doi: 10.1111/appy.12384. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Asia Pac Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32119764 Review.
-
[Clozapine in the treatment of mental manifestations of Parkinson disease].Rev Neurol (Paris). 1995 Apr;151(4):251-7. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1995. PMID: 7481376 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Second-Generation Antipsychotics Induce Metabolic Disruption in Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through an aPKC-Dependent Pathway.Cells. 2024 Dec 17;13(24):2084. doi: 10.3390/cells13242084. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39768174 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of clinical and pharmacological factors on the ratio of clozapine to norclozapine in psychiatric patients.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1518739. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1518739. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39840091 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and pharmacological factors influencing serum clozapine and norclozapine levels.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 27;15:1356813. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1356813. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38601469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fitton A, Heel RC. Clozapine. A review of its pharmacological properties, and therapeutic use in schizophrenia. Drugs. 1990;40(5):722–47. - PubMed
-
- Kapczinski F, Pfaffenseller B, Dursun SM, de Azevedo Cardoso T. Clozapine for bipolar disorder: what do we know thus far and what next? Bipolar Disord. 2021;23(2):115–6. - PubMed
-
- Tan MSA, Honarparvar F, Falconer JR, Parekh HS, Pandey P, Siskind DJ. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between clozapine and norclozapine serum levels and peripheral adverse drug reactions. Psychopharmacology. 2021;238(3):615–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

