Paneth cells in farm animals: current status and future direction
- PMID: 37582766
- PMCID: PMC10426113
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-023-00905-5
Paneth cells in farm animals: current status and future direction
Abstract
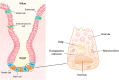
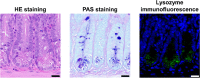
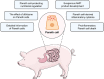
A healthy intestine plays an important role in the growth and development of farm animals. In small intestine, Paneth cells are well known for their regulation of intestinal microbiota and intestinal stem cells (ISCs). Although there has been a lot of studies and reviews on human and murine Paneth cells under intestinal homeostasis or disorders, little is known about Paneth cells in farm animals. Most farm animals possess Paneth cells in their small intestine, as identified by various staining methods, and Paneth cells of various livestock species exhibit noticeable differences in cell shape, granule number, and intestinal distribution. Paneth cells in farm animals and their antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are susceptible to multiple factors such as dietary nutrients and intestinal infection. Thus, the comprehensive understanding of Paneth cells in different livestock species will contribute to the improvement of intestinal health. This review first summarizes the current status of Paneth cells in pig, cattle, sheep, horse, chicken and rabbit, and points out future directions for the investigation of Paneth cells in the reviewed animals.
Keywords: Antimicrobial peptide; Farm animal; Intestinal organoid; Intestine; Paneth cell.
© 2023. Chinese Association of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
From birth to death: The hardworking life of Paneth cell in the small intestine.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 10;14:1122258. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1122258. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Farm Animal-derived Models of the Intestinal Epithelium: Recent Advances and Future Applications of Intestinal Organoids.Altern Lab Anim. 2020 Sep-Nov;48(5-6):215-233. doi: 10.1177/0261192920974026. Epub 2020 Dec 18. Altern Lab Anim. 2020. PMID: 33337913 Review.
-
Regulation of the Paneth cell niche by exogenous L-arginine couples the intestinal stem cell function.FASEB J. 2020 Aug;34(8):10299-10315. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902573RR. Epub 2020 Jun 17. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32725957
-
Intestinal organoids in farm animals.Vet Res. 2021 Feb 25;52(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13567-021-00909-x. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33632315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Paneth Cell: The Curator and Defender of the Immature Small Intestine.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 3;11:587. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00587. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32308658 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Extracellular Vesicles in Host-Microbiota Interactions.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024;73:475-520. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-62036-2_19. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2024. PMID: 39242390 Review.
-
The Joint Contribution of Host Genetics and Probiotics to Pig Growth Performance.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 7;13(2):358. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020358. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pluske JR, Hampson DJ, Williams IH. Factors influencing the structure and function of the small intestine in the weaned pig: a review. Livest Prod Sci. 1997;51(1–3):215–236. doi: 10.1016/S0301-6226(97)00057-2. - DOI
-
- Huang W, Kong D. The intestinal microbiota as a therapeutic target in the treatment of nafld and ald. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;135:111235. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111235. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

