Effect of curcumin supplementation on inflammatory status and muscle damage in competitive female soccer players: a placebo-controlled, singleblind, nonrandomized, crossover pilot study
- PMID: 37583070
- PMCID: PMC10440175
- DOI: 10.20463/pan.2023.0016
Effect of curcumin supplementation on inflammatory status and muscle damage in competitive female soccer players: a placebo-controlled, singleblind, nonrandomized, crossover pilot study
Abstract
Purpose: Curcumin, a major component of turmeric, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties, which are associated with protective effects against muscle damage. This study examined the effects of dietary curcumin on inflammation and muscle damage in female competitive soccer players.
Methods: A single-blinded, placebo-controlled, nonrandomized, crossover pilot study was conducted. Six competitive female soccer players (20.0 ± 2.0 yearsold) who participated in a 2-week preseason training program were assigned to two conditions: placebo and curcumin. The participants ingested a placebo or curcumin dosage (270 mg/day) during 2 weeks of preseason training, with 1 week of washout. Fasting blood samples were collected under resting conditions before (day 0) and after (day 15) the training period to examine changes in the concentration of interleukin 6 (IL-6), an inflammatory marker, and indices reflective of muscle damage.
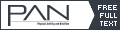
Results: Curcumin decreased the concentration of IL-6 released (mean decrease, -30.2 ± 28.1%), whereas no decrease was observed in the placebo condition (13.4 ± 17.4%). Changes in plasma IL-6 concentrations were significantly greater in the curcumin condition than in the placebo condition (p < 0.05). However, curcumin supplementation had no significant effects on muscle damage indices.
Conclusion: The present study shows that curcumin supplementation could attenuate inflammation, as indicated by IL-6 concentrations, in competitive female soccer players during the training period.
Keywords: athletes; curcumin; inflammation; muscle damage; plasma IL-6; supplementation.
Figures

References
-
- Clarkson PM, Sayers SP. Etiology of exercise-induced muscle damage. Can J Appl Physiol. 1999;24:234–48. - PubMed
-
- Cheung K, Hume P, Maxwell L. Delayed onset muscle soreness:treatment strategies and performance factors. Sports Med. 2003;33:145–64. - PubMed
-
- Maheshwari RK, Singh AK, Gaddipati J, Srimal RC. Multiple biological activities of curcumin: a short review. Life Sci. 2006;78:2081–7. - PubMed
-
- Ghandadi M, Sahebkar A. Curcumin: an effective inhibitor of interleukin-6. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23:921–31. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources