A Pilot Study to Assess Effect of Metformin Therapy on Prevention of Double Diabetes in Indian Adolescents with Type-1 Diabetes
- PMID: 37583410
- PMCID: PMC10424107
- DOI: 10.4103/ijem.ijem_46_23
A Pilot Study to Assess Effect of Metformin Therapy on Prevention of Double Diabetes in Indian Adolescents with Type-1 Diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: Increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Indian adolescents owing to the obesity epidemic leads to double diabetes (DD), which is associated with an increased risk of complications in type-1 diabetes (T1D). Metformin may be a useful intervention for the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance in T1D. We conducted this pilot randomized controlled trial with the objective of investigating the effect of metformin on insulin sensitivity in Indian adolescents with T1D.
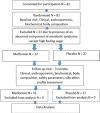
Method: This pilot randomized controlled trial was performed on 59 participants with T1D aged 10-19 years distributed uniformly by gender and puberty across two groups with a 3-month intervention period. The intervention group received metformin (weight less than 60 kg received 500 mg twice daily and more than 60 kg received 1 gm twice daily) and non-metformin group received standard of care for diabetes. Anthropometric, clinical details, biochemistry and insulin sensitivity indices (ISI) were evaluated using standard protocols at baseline and endline.
Result: 22.2% of subjects from non-metformin group and 12.5% from metformin group were at the risk of the development of DD. The odds ratio and relative risk for the development of DD in non-metformin subjects were 2.0 and 1.4, respectively, as compared to participants in metformin group. The mean improvement in ISI ranged from 1.4% to 4.6% in participants on metformin as opposed to deterioration of -2% to -14.1% in non-metformin group. On performing the paired sample t-test, the reduction in ISI in non-metformin group was significant.
Conclusion: Metformin may prevent deterioration in insulin sensitivity in Indian adolescents with T1D.
Keywords: Adolescents; double diabetes; insulin sensitivity; metabolic syndrome; metformin; type-1 diabetes.
Copyright: © 2023 Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
Effect of metformin adjunct therapy on cardiometabolic parameters in Indian adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024 Apr 19;5:1353279. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2024.1353279. eCollection 2024. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38706949 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of metformin on body mass index and glucose tolerance in obese adolescents with fasting hyperinsulinemia and a family history of type 2 diabetes.Pediatrics. 2001 Apr;107(4):E55. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.4.e55. Pediatrics. 2001. PMID: 11335776 Clinical Trial.
-
A Cross-Sectional Multicentre Study to Validate Insulin Sensitivity Index Cut-Offs for Detection of Metabolic Syndrome in Indian Adolescents with Type-1 Diabetes.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Jul-Aug;27(4):301-306. doi: 10.4103/ijem.ijem_411_22. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37867981 Free PMC article.
-
Repaglinide : a pharmacoeconomic review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(6):389-411. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200422060-00005. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004. PMID: 15099124 Review.
-
A Review of Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes: Is There a Place for Adjunctive Metformin?Diabetes Ther. 2018 Feb;9(1):349-361. doi: 10.1007/s13300-017-0333-9. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Diabetes Ther. 2018. PMID: 29139080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin Resistance in Adolescents and Youth With Type 1 Diabetes: A Review of Problems and Solutions.Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2023 Oct 26;16:11795514231206730. doi: 10.1177/11795514231206730. eCollection 2023. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37901890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of metformin adjunct therapy on cardiometabolic parameters in Indian adolescents with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024 Apr 19;5:1353279. doi: 10.3389/fcdhc.2024.1353279. eCollection 2024. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38706949 Free PMC article.
-
Double Trouble.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2023 May-Jun;27(3):189-191. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.379597. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37583408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Efficacy and Safety of Metformin as Add-on Therapy to Insulin in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025 Jul;8(4):e70060. doi: 10.1002/edm2.70060. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40512873 Free PMC article.
-
Double diabetes-when type 1 diabetes meets type 2 diabetes: definition, pathogenesis and recognition.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Feb 10;23(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02145-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38341550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; 2021.
-
- Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. Insulin resistance, the metabolic syndrome, and complication risk in type 1 diabetes:“Double diabetes”in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:707–12. - PubMed
-
- Pambianco G, Costacou T, Orchard TJ. The prediction of major outcomes of type 1 diabetes:A 12-year prospective evaluation of three separate definitions of the metabolic syndrome and their components and estimated glucose disposal rate:The Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study experience. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:1248–54. - PubMed
-
- Billow A, Anjana RM, Ngai M, Amutha A, Pradeepa R, Jebarani S, et al. Prevalence and clinical profile of metabolic syndrome among type 1 diabetes mellitus subjects in southern India. J Diabetes Complications. 2015;29:659–64. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources