Sharing leaky-integrate-and-fire neurons for memory-efficient spiking neural networks
- PMID: 37583415
- PMCID: PMC10423932
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1230002
Sharing leaky-integrate-and-fire neurons for memory-efficient spiking neural networks
Abstract
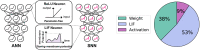
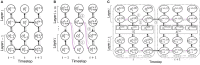
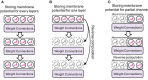
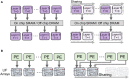
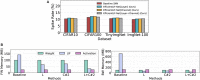
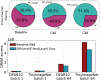
Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) have gained increasing attention as energy-efficient neural networks owing to their binary and asynchronous computation. However, their non-linear activation, that is Leaky-Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) neuron, requires additional memory to store a membrane voltage to capture the temporal dynamics of spikes. Although the required memory cost for LIF neurons significantly increases as the input dimension goes larger, a technique to reduce memory for LIF neurons has not been explored so far. To address this, we propose a simple and effective solution, EfficientLIF-Net, which shares the LIF neurons across different layers and channels. Our EfficientLIF-Net achieves comparable accuracy with the standard SNNs while bringing up to ~4.3× forward memory efficiency and ~21.9× backward memory efficiency for LIF neurons. We conduct experiments on various datasets including CIFAR10, CIFAR100, TinyImageNet, ImageNet-100, and N-Caltech101. Furthermore, we show that our approach also offers advantages on Human Activity Recognition (HAR) datasets, which heavily rely on temporal information. The code has been released at https://github.com/Intelligent-Computing-Lab-Yale/EfficientLIF-Net.
Keywords: energy-efficient deep learning; event-based processing; image recognition; neuromorphic computing; spiking neural network.
Copyright © 2023 Kim, Li, Moitra, Yin and Panda.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Akopyan F., Sawada J., Cassidy A., Alvarez-Icaza R., Arthur J., Merolla P., et al. . (2015). Truenorth: Design and tool flow of a 65 mw 1 million neuron programmable neurosynaptic chip. IEEE Transac. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circ. Syst. 34, 1537–1557. 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2474396 - DOI
-
- Anguita D., Ghio A., Oneto L., Parra X., Reyes-Ortiz J. L., et al. . (2013). “A public domain dataset for human activity recognition using smartphones,” in Esann 3.
-
- Che K., Leng L., Zhang K., Zhang J., Meng Q., Cheng J., et al. . (2022). “Differentiable hierarchical and surrogate gradient search for spiking neural networks,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 24975–24990.
-
- Chen Y., Yu Z., Fang W., Huang T., Tian Y. (2021). Pruning of deep spiking neural networks through gradient rewiring. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.04916.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

