Whole-brain structure-function coupling abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment: a study combining amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations and voxel-based morphometry
- PMID: 37583417
- PMCID: PMC10424122
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1236221
Whole-brain structure-function coupling abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment: a study combining amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations and voxel-based morphometry
Abstract
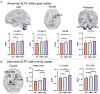
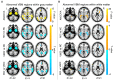
Alzheimer's disease (AD), one of the leading diseases of the nervous system, is accompanied by symptoms such as loss of memory, thinking and language skills. Both mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and very mild cognitive impairment (VMCI) are the transitional pathological stages between normal aging and AD. While the changes in whole-brain structural and functional information have been extensively investigated in AD, The impaired structure-function coupling remains unknown. The current study employed the OASIS-3 dataset, which includes 53 MCI, 90 VMCI, and 100 Age-, gender-, and education-matched normal controls (NC). Several structural and functional parameters, such as the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (ALFF), voxel-based morphometry (VBM), and The ALFF/VBM ratio, were used To estimate The whole-brain neuroimaging changes In MCI, VMCI, and NC. As disease symptoms became more severe, these regions, distributed in the frontal-inf-orb, putamen, and paracentral lobule in the white matter (WM), exhibited progressively increasing ALFF (ALFFNC < ALFFVMCI < ALFFMCI), which was similar to the tendency for The cerebellum and putamen in the gray matter (GM). Additionally, as symptoms worsened in AD, the cuneus/frontal lobe in the WM and the parahippocampal gyrus/hippocampus in the GM showed progressively decreasing structure-function coupling. As the typical focal areas in AD, The parahippocampal gyrus and hippocampus showed significant positive correlations with the severity of cognitive impairment, suggesting the important applications of the ALFF/VBM ratio in brain disorders. On the other hand, these findings from WM functional signals provided a novel perspective for understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms involved In cognitive decline in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amplitude of low frequency fluctuations; structure–function coupling; voxel-based morphometry; white matter.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Wang, Liu, Zhang, Hu, Wen, Li and Biswal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abramian D., Larsson M., Eklund A., Behjat H. (2020). Improved Functional Mri Activation Mapping in White Matter through Diffusion-Adapted Spatial Filtering. In 2020 Ieee 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (Isbi 2020) Vol 237, 118095.
-
- Alexopoulos P., Sorg C., Forschler A., Grimmer T., Skokou M., Wohlschlager A., et al. . (2012). Perfusion abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia in Alzheimer's disease measured by pulsed arterial spin labeling MRI. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 262, 69–77. doi: 10.1007/s00406-011-0226-2, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bao J. F., Tu H., Li Y. J., Sun J. B., Hu Z. G., Zhang F. S., et al. . (2022). Diffusion tensor imaging revealed microstructural changes in Normal-appearing white matter regions in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurosci. 16. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.837452, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

