Defining cardiac functional recovery in end-stage heart failure at single-cell resolution
- PMID: 37583573
- PMCID: PMC10426763
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-023-00260-8
Defining cardiac functional recovery in end-stage heart failure at single-cell resolution
Abstract
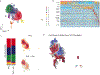
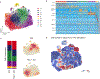
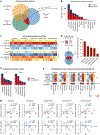
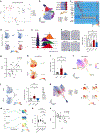
Recovery of cardiac function is the holy grail of heart failure therapy yet is infrequently observed and remains poorly understood. In this study, we performed single-nucleus RNA sequencing from patients with heart failure who recovered left ventricular systolic function after left ventricular assist device implantation, patients who did not recover and non-diseased donors. We identified cell-specific transcriptional signatures of recovery, most prominently in macrophages and fibroblasts. Within these cell types, inflammatory signatures were negative predictors of recovery, and downregulation of RUNX1 was associated with recovery. In silico perturbation of RUNX1 in macrophages and fibroblasts recapitulated the transcriptional state of recovery. Cardiac recovery mediated by BET inhibition in mice led to decreased macrophage and fibroblast Runx1 expression and diminished chromatin accessibility within a Runx1 intronic peak and acquisition of human recovery signatures. These findings suggest that cardiac recovery is a unique biological state and identify RUNX1 as a possible therapeutic target to facilitate cardiac recovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
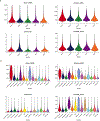

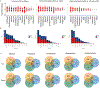
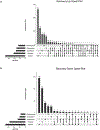

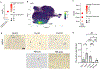






References
-
- Jessup M & Brozena S Heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med 348, 2007–2018 (2003). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P30 AR073752/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135121/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151078/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139714/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL151924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL161185/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL156667/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007576/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX002291/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL125241/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138466/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM126112/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK091317/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
