Discovery of MK-8768, a Potent and Selective mGluR2 Negative Allosteric Modulator
- PMID: 37583812
- PMCID: PMC10424309
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00210
Discovery of MK-8768, a Potent and Selective mGluR2 Negative Allosteric Modulator
Abstract
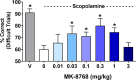
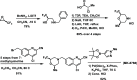
Glutamate plays a key role in cognition and mood, and it has been shown that inhibiting ionotropic glutamate receptors disrupts cognition, while enhancing ionotropic receptor activity is pro-cognitive. One approach to elevating glutamatergic tone has been to antagonize presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 (mGluR2). A desire for selectivity over the largely homologous mGluR3 motivated a strategy to achieve selectivity through the identification of mGluR2 negative allosteric modulators (NAMs). Extensive screening and optimization efforts led to the identification of a novel series of 4-arylquinoline-2-carboxamides. This series was optimized for mGluR2 NAM potency, clean off-target activity, and desirable physical properties, which resulted in the identification of improved C4 and C7 substituents. The initial lead compound from this series was Ames-positive in a single strain with metabolic activation, indicating that a reactive metabolite was likely responsible for the genetic toxicity. Metabolic profiling and Ames assessment across multiple analogs identified key structure-activity relationships associated with Ames positivity. Further optimization led to the Ames-negative mGluR2 negative allosteric modulator MK-8768.
© 2023 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): All authors were employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA at the time of their contribution to this work.
Figures
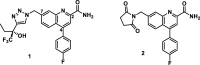

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

