miR-9-5p expression is associated with vascular invasion and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma, and in vitro verification
- PMID: 37584711
- PMCID: PMC11796758
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-05257-1
miR-9-5p expression is associated with vascular invasion and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma, and in vitro verification
Abstract
Purpose: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common liver malignancy. Early vascular invasion (VI) has been associated with poor prognosis in HCC patients. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a significant role in the emergence and development of many tumor types.
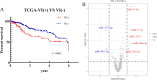
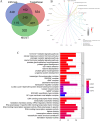
Methods: Differential expression analysis of miRNAs related to VI was performed based on data from the TCGA database, and survival-associated miRNAs identified. We identified miR-9-5p as a survival-related miRNA and verified its expression in 61 clinical samples using quantitative real-time PCR. We further performed functional enrichment analysis, protein-protein interaction analysis, univariate and multivariate analysis of the survival-related miRNAs, and cell function assays.
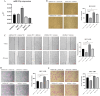
Results: In this study, we identified miR-9-5p that could predict VI and prognosis in HCC patients. Cellular experiments demonstrated that downregulation of miR‑9‑5p inhibits migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of HCC cells. Further, we explored and verified the possible mechanism through which miR-9-5p is involved in HCC progression. Univariate and multivariate analysis revealed that miR-9-5p was an independent risk factor for HCC. Finally, the nomogram based on miR-9-5p showed a good predictive value of HCC survival.
Conclusions: MiR-9-5p is associated with VI in HCC, and higher expression of miR-9-5p indicates poor prognosis in HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis; TCGA; Vascular invasion; miRNAs.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA LNC-POTEM-4 promotes HCC progression via the LNC-POTEM-4/miR-149-5p/Wnt4 signaling axis.Cell Signal. 2024 Dec;124:111412. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111412. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 39278454
-
miR-32-5p suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the GSK3β/NF-κB signaling.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025 Apr 1;57(7):1125-1138. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2025038. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025. PMID: 40170617 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR-3130-5p Enhances Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth by Suppressing Ferredoxin 1 : miR-3130-5p Enhances HCC Growth via Inhibiting FDX1.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024;17:e18761429358008. doi: 10.2174/0118761429358008250305070518. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 40103455
-
The Protective Role of miR-125b in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Unraveling Tumor-Suppressive Mechanisms.Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(6):663-671. doi: 10.2174/0115665240304247240529074123. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 38859784 Review.
-
Circulating miR-542-3p as a Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jul;29(14):e70748. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70748. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40717227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

