Efficacy of Regimens in the Treatment of Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: A Network Meta-analysis
- PMID: 37584857
- PMCID: PMC10499777
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-023-01459-5
Efficacy of Regimens in the Treatment of Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: A Network Meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) is a highly heterogeneous autoimmune condition with clinical and genetic characteristics that fall between those of type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus; therefore, there are no uniform criteria for the selection of therapeutic agents. We conducted a network meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of various therapeutic agents for LADA by comparing their effects on various indicators used to reflect LADA.
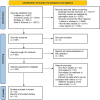
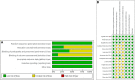
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase and Web of Science databases from their inception to March 2023 and collected data from 14 randomized controlled trials on glucose-lowering drugs for LADA, including 23 studies and 15 treatment regimens. The effectiveness of drugs was ranked and evaluated by combining surface under the cumulative ranking (SUCRA) plots and forest plots. Factors that may influence study heterogeneity were also searched and analyzed by combining subgroup analysis, publication bias, funnel plots and sensitivity analysis.
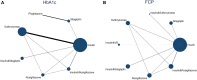
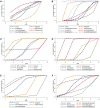
Results: The results of the network meta-analysis showed that insulin had the most significant effect on the control of change from baseline in glycosylated hemoglobin, type A1 (ΔHbA1c). Insulin combined with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors performed the best in reducing fasting blood glucose and body mass index. Treatment regimens involving thiazolidinediones were the most advantageous in HbA1c, fasting C-peptide and postprandial C-peptide control. Longer dosing may be more beneficial in maintaining islet β-cell function in the LADA population.
Conclusion: LADA is an immune condition with high heterogeneity, and treatment should be administered according to the C-peptide level of the LADA population. For this population with LADA with a certain level of β-cell function, combinations of insulin with DPP-4 inhibitors or thiazolidinediones probably can be more effective treatment options to maintain islet function and normal blood glucose.
Trial registration: PROSPERO CRD42023410795.
Keywords: C-peptide; Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults; Network meta-analysis; Randomized controlled trials.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin and insulin for latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes Investig. 2022 Sep;13(9):1506-1519. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13814. Epub 2022 May 6. J Diabetes Investig. 2022. PMID: 35445591 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Berberine Plus Inulin on Diabetes Care in Patients With Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 15;13:876657. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.876657. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35784546 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor sitagliptin maintains β-cell function in patients with recent-onset latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: one year prospective study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 May;99(5):E876-80. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3633. Epub 2014 Jan 16. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24432999 Clinical Trial.
-
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: Current Status and New Horizons.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2018 Jun;33(2):147-159. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.147. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2018. PMID: 29947172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Islet Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults Taking Sitagliptin: A Randomized Trial.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Mar 25;106(4):e1529-e1541. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab026. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33475138 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Exploring a Synergistic Approach: Dual GLP-1 Agonist Combined with Degludec Basal Insulin for Early Type 1 Diabetes Treatment and its Impact on Albumin-Insulin Producing Cells Expression.Adv Pharm Bull. 2024 Jul;14(2):262-265. doi: 10.34172/apb.2024.040. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Adv Pharm Bull. 2024. PMID: 39206389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petreski H. Misdiagnosed patient with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (case report) Georgian Med News. 2018;277:31–35. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. 1999. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/66040. Acessed 17 June 2012.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

