Profiling single cancer cell metabolism via high-content SRS imaging with chemical sparsity
- PMID: 37585522
- PMCID: PMC10431717
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg6061
Profiling single cancer cell metabolism via high-content SRS imaging with chemical sparsity
Abstract
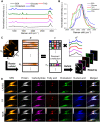
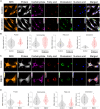
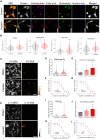
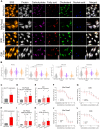
Metabolic reprogramming in a subpopulation of cancer cells is a hallmark of tumor chemoresistance. However, single-cell metabolic profiling is difficult because of the lack of a method that can simultaneously detect multiple metabolites at the single-cell level. In this study, through hyperspectral stimulated Raman scattering (hSRS) imaging in the carbon-hydrogen (C-H) window and sparsity-driven hyperspectral image decomposition, we demonstrate a high-content hSRS (h2SRS) imaging approach that enables the simultaneous mapping of five major biomolecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, fatty acids, cholesterol, and nucleic acids at the single-cell level. h2SRS imaging of brain and pancreatic cancer cells under chemotherapy revealed acute and adapted chemotherapy-induced metabolic reprogramming and the unique metabolic features of chemoresistance. Our approach is expected to facilitate the discovery of therapeutic targets to combat chemoresistance. This study illustrates a high-content, label-free chemical imaging approach that measures metabolic profiles at the single-cell level and warrants further research on cellular metabolism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fast vibrational imaging of single cells and tissues by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Aug 19;47(8):2282-90. doi: 10.1021/ar400331q. Epub 2014 May 28. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24871269 Free PMC article.
-
Fingerprint-to-CH stretch continuously tunable high spectral resolution stimulated Raman scattering microscope.J Biophotonics. 2019 Sep;12(9):e201900028. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201900028. Epub 2019 Jun 14. J Biophotonics. 2019. PMID: 31081280
-
Live-cell stimulated Raman scattering imaging of alkyne-tagged biomolecules.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014 Jun 2;53(23):5827-31. doi: 10.1002/anie.201400328. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014. PMID: 24753329
-
Imaging chemistry inside living cells by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy.Methods. 2017 Sep 1;128:119-128. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.07.020. Epub 2017 Jul 23. Methods. 2017. PMID: 28746829 Review.
-
Live-Cell Bioorthogonal Chemical Imaging: Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy of Vibrational Probes.Acc Chem Res. 2016 Aug 16;49(8):1494-502. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00210. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Acc Chem Res. 2016. PMID: 27486796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-content stimulated Raman histology of human breast cancer.Theranostics. 2024 Jan 27;14(4):1361-1370. doi: 10.7150/thno.90336. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38389847 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical imaging for biological systems: techniques, AI-driven processing, and applications.J Mater Chem B. 2025 Jun 18;13(24):6916-6948. doi: 10.1039/d4tb02876g. J Mater Chem B. 2025. PMID: 40433910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced vibrational microscopes for life science.Nat Methods. 2025 May;22(5):912-927. doi: 10.1038/s41592-025-02655-w. Epub 2025 May 13. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 40360912 Review.
-
Two-dimensional bond-selective fluorescence spectroscopy: violations of the resonance condition, vibrational cooling rate dispersion, and super-multiplex imaging.Chem Sci. 2025 Jul 30;16(33):14905-14918. doi: 10.1039/d5sc02628h. eCollection 2025 Aug 20. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40800048 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired resistance in cancer: towards targeted therapeutic strategies.Nat Rev Cancer. 2025 Aug;25(8):613-633. doi: 10.1038/s41568-025-00824-9. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40461793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- K. D. Miller, L. Nogueira, A. B. Mariotto, J. H. Rowland, K. R. Yabroff, C. M. Alfano, A. Jemal, J. L. Kramer, R. L. Siegel, Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 69, 363–385 (2019). - PubMed
-
- J. Kopecka, P. Trouillas, A. C. Gasparovic, E. Gazzano, Y. G. Assaraf, C. Riganti, Phospholipids and cholesterol: Inducers of cancer multidrug resistance and therapeutic targets. Drug Resist. Updat. 49, 100670 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

