Metabolomics-directed nanotechnology in viral diseases management: COVID-19 a case study
- PMID: 37587394
- PMCID: PMC10539420
- DOI: 10.1007/s43440-023-00517-w
Metabolomics-directed nanotechnology in viral diseases management: COVID-19 a case study
Abstract
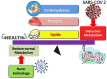
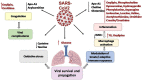
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is currently regarded as the twenty-first century's plague accounting for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Besides its reported symptoms affecting the respiratory tract, it was found to alter several metabolic pathways inside the body. Nanoparticles proved to combat viral infections including COVID-19 to demonstrate great success in developing vaccines based on mRNA technology. However, various types of nanoparticles can affect the host metabolome. Considering the increasing proportion of nano-based vaccines, this review compiles and analyses how COVID-19 and nanoparticles affect lipids, amino acids, and carbohydrates metabolism. A search was conducted on PubMed, ScienceDirect, Web of Science for available information on the interrelationship between metabolomics and immunity in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection and the effect of nanoparticles on metabolite levels. It was clear that SARS-CoV-2 disrupted several pathways to ensure a sufficient supply of its building blocks to facilitate its replication. Such information can help in developing treatment strategies against viral infections and COVID-19 based on interventions that overcome these metabolic changes. Furthermore, it showed that even drug-free nanoparticles can exert an influence on biological systems as evidenced by metabolomics.
Keywords: COVID-19; Metabolomics; Nanoparticles; SARS-CoV-2; Viral infections.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal's policy on disclosure of potential conflicts of interest, and they all wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
All authors have read the journal’s authorship statement and agree to it. By your journal’s policy, we confirm that the material contained in the manuscript is original and has not been published and is not being submitted elsewhere. The authors qualify for authorship and have no financial or personal relationships that might lead to a conflict of interest. This manuscript is being submitted online in accordance with your policies for this type of submission. The Authors hereby grant the Journal full and exclusive rights to the manuscript, all revisions, and the full copyright. The Journal rights include but are not limited to the following: (1) to reproduce, publish, sell, and distribute copies of the manuscript, selections of the manuscript, and translations and other derivative works based upon the manuscript, in print, audio-visual, electronic, or by any media now or hereafter known or devised; (2) to license reprints of the manuscript to third persons for educational photocopying; (3) to license others to create abstracts of the manuscript and to index the manuscript; (4) to license secondary publishers to reproduce the manuscript in print, microform, or any computer-readable form, including electronic on-line databases; and (5) to license the manuscript for document delivery. These exclusive rights run the full term of the copyright and all renewals and extensions thereof.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
